face_recognition使用python调用记录
一、查看本机配置和检查dlib是否能用gpu,不能用gpu也行,就是处理速度不同,不在乎的话以下检查可跳过。
我的显卡:GTX750TI
本机原来就有装cuda、cudnn(原来供tensorflow gpu使用)
1、查看cuda版本:
命令行输入:nvcc --version

查到是v10.0版本;
2、查看cudnn版本
输入文件地址打开查看
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.0\include\cudnn.h
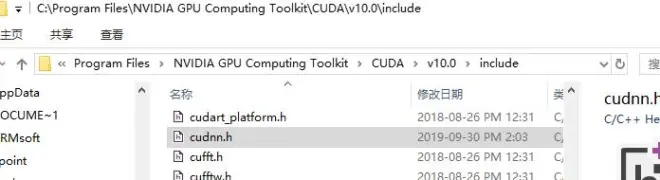

查到是7.6.5版本。
2、dlib是本地编译安装的(看我之前安装配置的视频可见,据说只有本地编译才能使用GPU)
输入命令查看dlib是否能用GPU:
>python
>>> import dlib
>>> print(dlib.DLIB_USE_CUDA)

OK可以使用gpu。
顺便检查一下tensorflow版本,这步是多余的,我只是忘了我装的TF版本。
>>> tf.__version__

二、开始测试python调用face_recognition功能
1、打开python编辑器(我用的是jupyter lab,需安装。)
在做测试的工程文件附近空白处按住shift键,同时点击鼠标右键,在弹出菜单点击箭头处打开命令行终端,输入jupyter lab回车执行:


即可打开编辑器,新建一个可即时运行python3的文件mian.ipynb:
2、写入测试命令:
import face_recognition#导入人脸识别库
import numpy as np
#人脸定位框
image = face_recognition.load_image_file('./pictures/unknown_pictures/1.jpg')#读取一张图片
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(image)#执行检测并返回人脸位置
print('检测到有 {} 人'.format(len(face_locations)))
print(face_locations)

#人脸对比
known_image = face_recognition.load_image_file('./pictures/known_people/TaylorSwift.jpg')
known_image_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(known_image)
unknown_image = face_recognition.load_image_file('./pictures/unknown_pictures/2.jpg')
unknown_image_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(unknown_image)[0]
result = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_image_encoding,unknown_image_encoding)
#print(unknown_image_encoding)
print(result)

#人脸截取
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt#绘图库
unknown_image = face_recognition.load_image_file('./pictures/unknown_pictures/4.jpg')#读取一张图片
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(unknown_image)#执行检测并返回人脸位置
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))#figsize里面的系数越大,画布越大,当然运行时间越长
plt.imshow(unknown_image)#处理将要显示的图片
plt.show()#显示主图片
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))#figsize里面的系数越大,画布越大,当然运行时间越长
for i,face_location in enumerate(face_locations):
top, right, bottom, left = face_location
#print(i,top, right, bottom, left)
plt.subplot(350+i+1)
plt.imshow(unknown_image[top:bottom,left:right])#处理将要显示经切片的图片,numpy.ndarray的切片方法
plt.show()#显示图片
type(unknown_image)

#人脸画框,注释
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt#绘图库
unknown_image = face_recognition.load_image_file('./pictures/unknown_pictures/4.jpg')#读取一张图片
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(unknown_image, number_of_times_to_upsample=0, model="cnn")#执行HOG模型检测并返回人脸位置(相对慢),使用神经网络检测number_of_times_to_upsample=0, model="cnn",初加载会比较慢,加载后再检测就很快了。
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))#figsize里面的系数越大,画布越大,当然运行时间越长
plt.imshow(unknown_image)#处理将要显示的图片
for i,face_location in enumerate(face_locations):
top, right, bottom, left = face_location
#print(i,top, right, bottom, left)
#画定位框,plt.Rectangle((起点),框尺寸)
people_color = '#%06x'%np.random.randint(0xffffff)#随机6个十六进制的颜色颜色
plt.text(left, top-8, i, bbox={'facecolor':people_color, 'alpha':0.5, 'pad':1})#添加注释
plt.gca().add_patch(plt.Rectangle((left, top), bottom - top, right - left,fill=False,linewidth = 2,edgecolor = people_color))#执行画框
plt.show()#显示图片
type(unknown_image)

#检测并绘制关键点
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt#绘图库
image = face_recognition.load_image_file('./pictures/unknown_pictures/10.jpg')#读取一张图片
face_landmarks_list = face_recognition.face_landmarks(image)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))#figsize里面的系数越大,画布越大,当然运行时间越长
plt.imshow(image)#处理将要显示的图片
a = face_landmarks_list[0]
for wuguan in a.values():
for sxy in wuguan:
#print(sxy)
plt.scatter(sxy[0], sxy[1], c='b', s=5)#执行画点
plt.show()#显示图片

#摄像头检测人脸
import face_recognition
import numpy as np
import CV2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
def CV2ImgAddText1(img, text, left, top, textColor=(0, 255, 0), textSize=20):#opencv不支持中文,得用这个函数解决
fontText = ImageFont.truetype("./simsun.ttc", textSize)
img_pil = Image.fromarray(img)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_pil)
draw.text((left, top), text, fill = textColor, font=fontText)
img = np.array(img_pil)
return img
# This is a super simple (but slow) example of running face recognition on live video from your webcam.
# There's a second example that's a little more complicated but runs faster.
# PLEASE NOTE: This example requires OpenCV (the `CV2` library) to be installed only to read from your webcam.
# OpenCV is *not* required to use the face_recognition library. It's only required if you want to run this
# specific demo. If you have trouble installing it, try any of the other demos that don't require it instead.
# Get a reference to webcam #0 (the default one)
video_capture = CV2.VideoCapture(0)
# Load a sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
obama_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("./pictures/known_people/TaylorSwift.jpg")
obama_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(obama_image)[0]
# Load a second sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
biden_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("./pictures/known_people/Clinton.jpg")
biden_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(biden_image)[0]
# Create arrays of known face encodings and their names
known_face_encodings = [
obama_face_encoding,
biden_face_encoding
]
known_face_names = [
"TaylorSwift",
"Clinton"
]
# Initialize some variables
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
face_names = []
process_this_frame = True
while True:
# Grab a single frame of video
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
# Resize frame of video to 1/4 size for faster face recognition processing
small_frame = CV2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
# Convert the image from BGR color (which OpenCV uses) to RGB color (which face_recognition uses)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:, :, ::-1]
# Only process every other frame of video to save time
if process_this_frame:
# Find all the faces and face encodings in the current frame of video
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame, model="cnn")#使用神经网络检测
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# See if the face is a match for the known face(s)
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
name = "Unknown"
# # If a match was found in known_face_encodings, just use the first one.
# if True in matches:
# first_match_index = matches.index(True)
# name = known_face_names[first_match_index]
# Or instead, use the known face with the smallest distance to the new face
face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
best_match_index = np.argmin(face_distances)
if matches[best_match_index]:
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]
face_names.append(name)
process_this_frame = not process_this_frame
# Display the results
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):#[face_locations, face_names]
# Scale back up face locations since the frame we detected in was scaled to 1/4 size
top *= 4
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
left *= 4
# Draw a box around the face
CV2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# Draw a label with a name below the face
CV2.rectangle(frame, (left, bottom - 35), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), CV2.FILLED)
#font = CV2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX
#CV2.putText(frame, name, (left + 6, bottom - 6), font, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), 1)
frame = CV2ImgAddText1(frame, name, left, bottom-25, textColor=(0, 255, 0),textSize=20)#opencv不支持中文,得用这个函数解决
# Display the resulting image
CV2.imshow('Video', frame)
# Hit 'q' on the keyboard to quit!
if CV2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# Release handle to the webcam
video_capture.release()
CV2.destroyAllWindows()

#动态截屏检测
from PIL import ImageGrab
import face_recognition
import numpy as np
import CV2
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
def CV2ImgAddText1(img, text, left, top, textColor=(0, 255, 0), textSize=20):#CV2.putText不支持中文,得用这个函数解决
fontText = ImageFont.truetype("./simsun.ttc", textSize)
img_pil = Image.fromarray(img)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_pil)
draw.text((left, top), text, fill = textColor, font=fontText)
img = np.array(img_pil)
return img
# Load a sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
obama_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("./pictures/known_people/TaylorSwift.jpg")
TaylorSwift_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(obama_image)[0]
# Load a second sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
biden_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("./pictures/known_people/Clinton.jpg")
Clinton_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(biden_image)[0]
# Load a second sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
biden_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("./pictures/known_people/马云.jpg")
mayun_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(biden_image)[0]
# Load a second sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
biden_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("./pictures/known_people/成龙.jpg")
chenglong_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(biden_image)[0]
# Create arrays of known face encodings and their names
known_face_encodings = [
TaylorSwift_face_encoding,
Clinton_face_encoding,
mayun_face_encoding,
chenglong_face_encoding
]
known_face_names = [
"Taylor Swift",
"Clinton",
"马云",
"成龙"
]
# Initialize some variables
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
face_names = []
process_this_frame = True
while True:
# Grab a single frame of video
frame = np.array(ImageGrab.grab(bbox=(0, 40, 800, 600)))#动态截屏
# Resize frame of video to 1/4 size for faster face recognition processing
small_frame = CV2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.45, fy=0.45)
# Convert the image from BGR color (which OpenCV uses) to RGB color (which face_recognition uses)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame
# Only process every other frame of video to save time
if process_this_frame:
# Find all the faces and face encodings in the current frame of video
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame, model="cnn")#使用神经网络检测
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# See if the face is a match for the known face(s)
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_face_encodings, face_encoding, tolerance=0.6)
name = "Unknown"
# # If a match was found in known_face_encodings, just use the first one.
# if True in matches:
# first_match_index = matches.index(True)
# name = known_face_names[first_match_index]
# Or instead, use the known face with the smallest distance to the new face
face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
best_match_index = np.argmin(face_distances)
if matches[best_match_index]:
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]
face_names.append(name)
process_this_frame = not process_this_frame
# Display the results
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
# Scale back up face locations since the frame we detected in was scaled to 1/4 size
top = int(top * 0.9)
right = int(right * 1)
bottom = int(bottom * 1.1)
left = int(left * 0.98)
# Draw a box around the face
CV2.rectangle(small_frame, (left, top), (right, bottom-5), (10, 0, 100), 1)
# Draw a label with a name below the face
CV2.rectangle(small_frame, (left, bottom - 10), (right, bottom), (10, 0, 100), CV2.FILLED)
font = CV2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX
#CV2.putText(frame, name, (left + 6, bottom - 6), font, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), 1)
small_frame = CV2ImgAddText1(small_frame, name, left, bottom-10, textColor=(255, 2, 255),textSize=10)#CV2.putText不支持中文,得用这个函数解决
small_frame = CV2.resize(small_frame, (800, 550))
# Display the resulting image
CV2.imshow('Video', small_frame[:,:,::-1])
# Hit 'q' on the keyboard to quit!
if CV2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
CV2.destroyAllWindows()


