试译 | 九宫格问题——海杜克《美杜莎的面具》
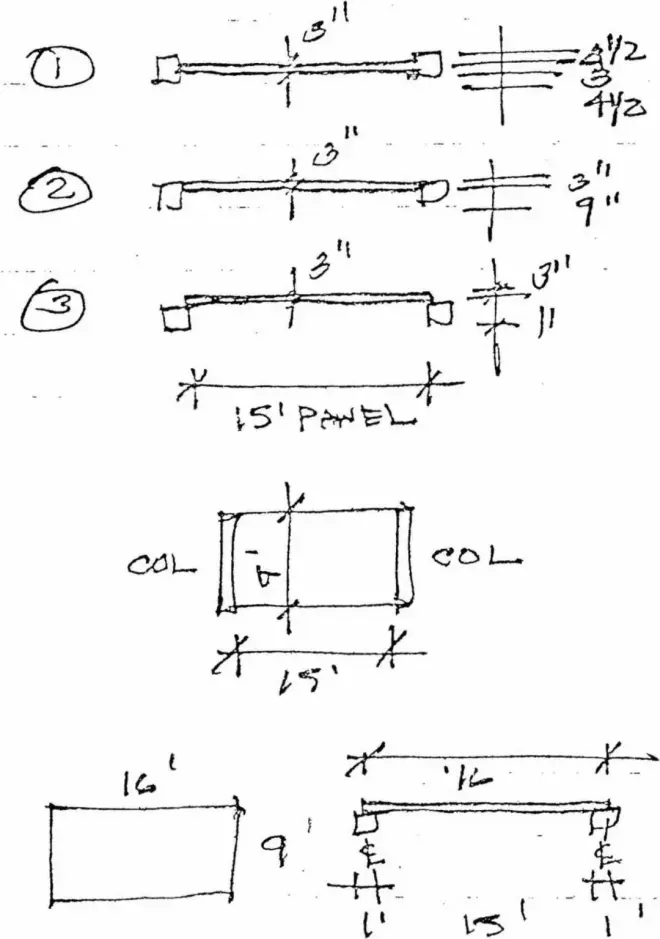
The Nine square Problem is used as a pedagogical tool in the introduction of architecture to new students. Working within the problem the student begins to discover and understand the elements of architecture. Grid, frame, post, beam, panel, center, periphery, field, edge, line, plane, volume, extension, compression, tension, shear, etc. The student begins to probe the meaning of plan, elevation, section and details. He learns to draw. He begins to comprehend the relationships between two dimensional drawings, axonometric projections, and three dimensional (model) form. The student studies and draws his scheme in plan and in axonometric, and searches out the three-dimensional implications in the model. An understanding of the elements is revealed, an idea of fabrication emerges.
The Nine square Problem
Build a model at ¼”=1’–0 scale of the following. Make a 30/60 isometric drawing in pencil on tracing vellum of the following. The constructed model and the drawing will be the basic working tools for the research and study of the Nine square problem.
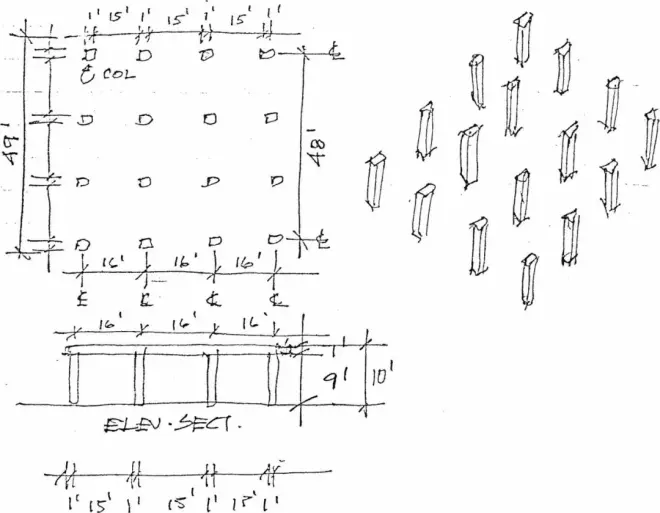
Columns – white, base board – black, panels – gray. One grid 15’ divided into 5’s and 3’s. One grid 16’ divided into 1’s and 2’s.
The nine square falls between two poles, one of complete fluidity and one of complete containment.
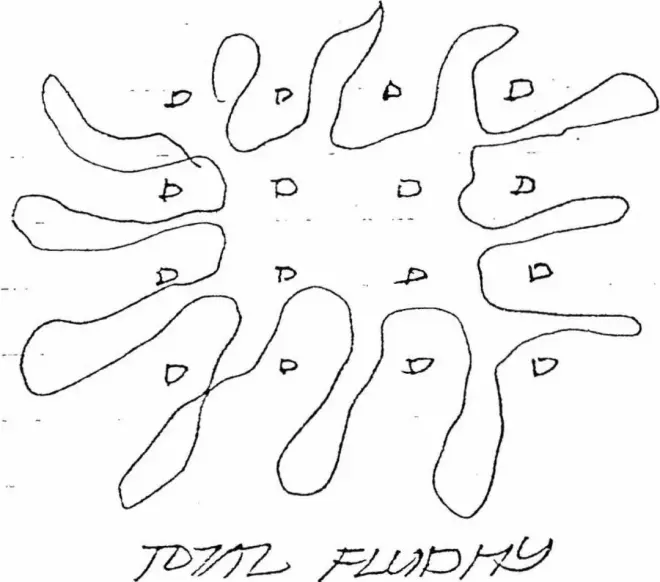
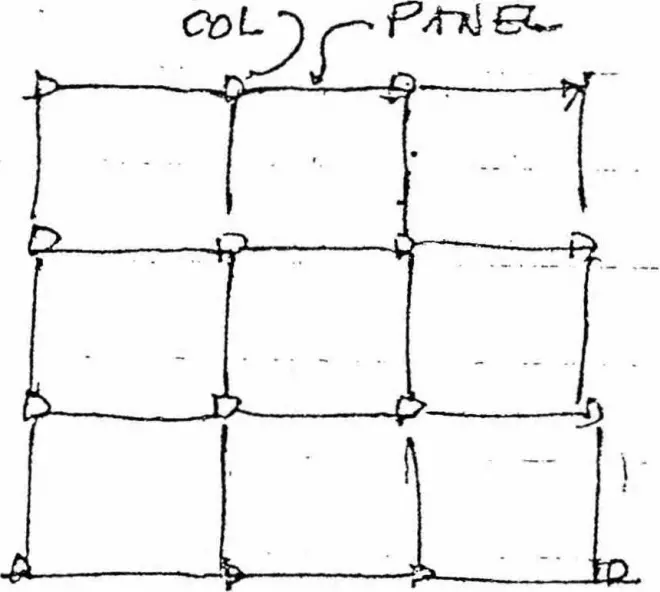
The idea of The center and the periphery. 1 center cell and 8 peripheral cells.
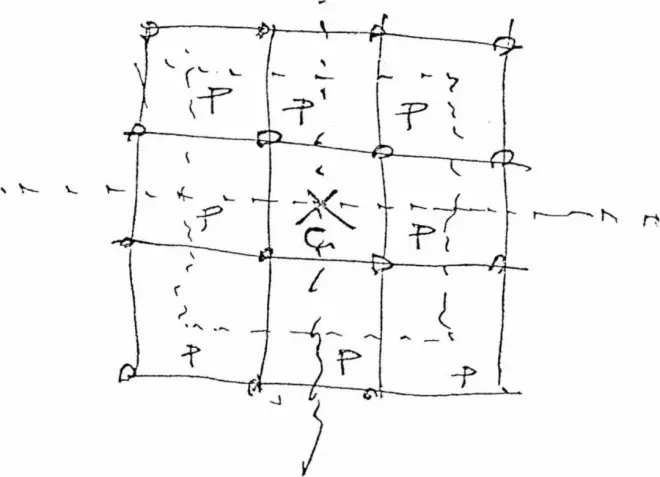
Take the full panels (model) and study spatial relationships within the 9 square grid (16 columns). Then take the scheme and drew up in pencil in axonometric. This form of study will be carried in through the following problems.
1. Full panels.
2. ½ Panels (Horizontal/Vertical).
3. Combine Full and Half Panels.
4. Curved Panels and half Circle.
5. Combine Full and Curved Panels.
6. Combine Full, Half, and Curved Panels.
7. Full Panel at 45°or 60°. Or, 45°and 60°.
8. Combine Full Panels 90°and 45°or 60°。
9. Combine Full (90°,60°,45°) ½, and Curved Panels.
10. Above systems off the column frame (not touching columns).
11. Make series of volumes (circle, square, triangle) ranging from 1’ square, 1’ diameter, 1’ triangular to 10’ square, etc. and ranging from 1’ vertical height to 10’ vertical height.
12. Combine columns with panels in a series of different combinations.
13. Build stairs, ramps, straight run stair, U run stair, circular stair, straight run ramp, U run ramp.
14. Build second storey frame and continue study.
15. Build third storey frame and continue study.
16. Build roof structures ½ circle, ½ lozenge or ½ diamond, ½ square.
17. Combine all systems.
以下为尝试翻译稿,请谨慎阅读。如有误导,概不负责。

九宫格问题被用作向新生介绍建筑学的教学工具。在(九宫格)问题中,学生开始发现和理解建筑的元素,网格、框架、柱、梁、板、中心、外围、场域、边缘、线、面、体、扩展、压缩、紧张、剪切等。学生们开始探索平面、立面、剖面以及细部节点的意义。他们学会了如何绘制。他们开始理解二维图纸,轴测投影及三维(模型)之间的关系。学生们在平面和轴测图上研究和绘制自己的方案,并通过模型探究其三维结果。于是,对要素的理解开始明晰,建构的理念开始涌现。
九宫格问题
按1/4英寸=1.0英尺的比例建立如下模型。用铅笔在描图纸上按下图绘制30/60度等轴测。这个模型和图纸将作为研究和学习九宫格问题的基本操作工具。
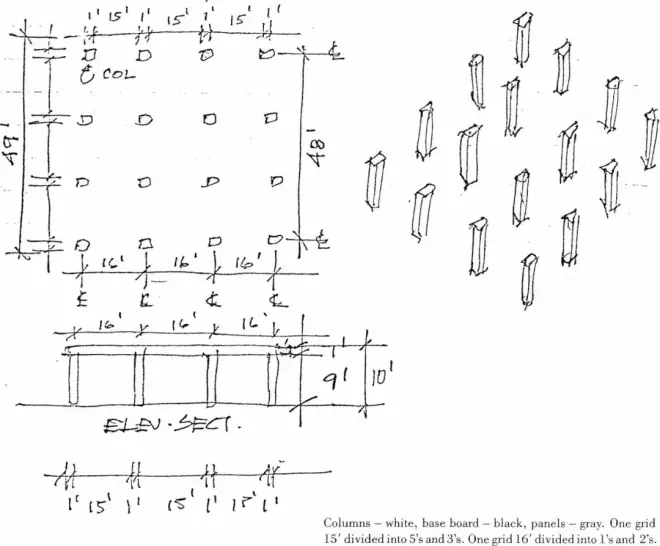
柱-白色,底板-黑色,隔板-灰色。一个15英尺网格分成5等份和3等份,一个16英尺网格分成1等份和2等份。
九个方格介于完全自由流动与完全独立封闭的两极之间。


封闭
中心与外围的概念。一个中心网格,八个外围网格。

取完整的隔墙(模型),在9个方格(16根柱)中研究空间关系。然后将方案用铅笔在轴测图中绘制。这种形式研究可以通过以下问题进行下去。
1. 完整隔板(墙)。
2. 1/2隔墙(水平向/纵向)。
3. 完整隔墙和1/2隔墙组合。
4. 曲墙与半圆隔墙组合。
5. 完整隔墙与曲墙组合。
6. 隔墙,半墙与曲墙组合。
7. 完整隔墙转45°或60°,或45°与60°隔墙组合。
8. 完整隔墙与45°或60°隔墙组合。
9. 完整隔墙(90°,60°,45°)的1/2与曲墙组合。
10. 将以上系统脱离柱网框架(不触及那些柱子)。
11. 放置一系列体量(圆形、方形或三角形),三角形、正方形体量底边或圆形直径)从1英尺到10英尺不等,高度也从1英尺到10英尺不等。
12. 将柱与隔墙板以一系列不同的组合方式联结。
13. 创建楼梯,坡道,直跑楼梯,U形楼梯,圆形楼梯,直跑坡道,U形坡道。
14. 创建第二层框架并延续之前的研究。
15. 创建第三层框架并延续之前的研究。
16. 建立1/2圆,1/2菱形,1/2方形屋顶结构。
17. 联结以上系统。

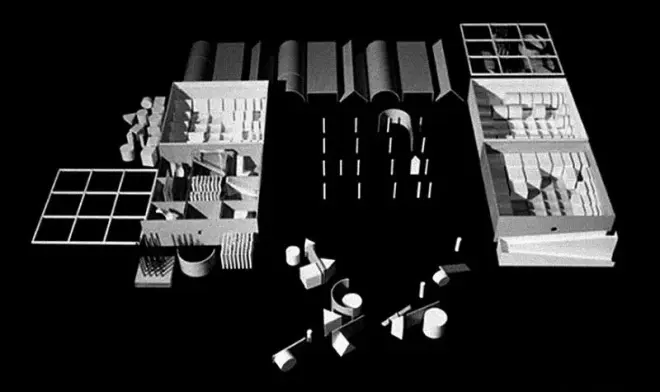

1. 本篇英文原稿及插图除特别注明外均来自于Mask of Medusa,by John Hejduk;
2. ¼”=1’–0,比例尺表示方法,即¼”=1’0”,¼英寸=1英尺的比例。
3. panel, a section or division of a wall, ceiling, or other surface. 因此这里翻作隔墙。

