【图像加密】基于正交拉丁方置乱+混沌图像加密解密含Matlab源码
1 简介
提出了一种基于正交拉丁方置乱+混沌的图像置乱加密算法.借助MATLAB2014软件平台编程实现,并研究了加密算法的抗破损能力.实验结果表明:该算法的加密效果良好,图像的抗破损能力强.
2 部分代码
% RegisterFourierMellin% This code is the result of my messing around with Matlab investigating % various image registration techniques. I came across the excellent % (although perhaps a little messy and buggy) fm_gui_v2 from Adam Wilmer% here:% http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/loadFile.do?objectId=3000&objectType=file% Because my needs are essentially the algorithm itself in a neat and tidy% format to enable an easier conversion to C++, I've extracted what I think% is the essence of the Fourier Mellin method into this file. Obviously% I haven't included a GUI. In order to test it, you need to set the first% two statements to load in 2 image files of the same size, in 8 bit grayscale.% I took lena and then used Gimp to rotate/shift/crop at various angles.% It isn't sub-pixel accurate, although I'm aware of methods to achieve% this by extracting the peaks around the peak of the phase correlation and% finding the maxima (least squares perhaps). % The methods towards the end of the program are cribbed directly from% Adam's version. I'm new to Matlab (been playing with it for less than% a fortnight), so I wasn't able to get my head around his log polar transform% or the final "blending" of the two images together.% I'd like to thank Adam for publishing his version. Without it I'd never% have known I had to take the log polar transform of the magnitude of the% FFT, rather than the log polar transform of the original image!function combImage=RegnisterFourierMellin(I1,I2) % The procedure is as follows (note this does not compute scale) % (1) Read in I1 - the image to register against % (2) Read in I2 - the image to register % (3) Take the FFT of I1, shifting it to center on zero frequency % (4) Take the FFT of I2, shifting it to center on zero frequency % (5) Convolve the magnitude of (3) with a high pass filter % (6) Convolve the magnitude of (4) with a high pass filter % (7) Transform (5) into log polar space % (8) Transform (6) into log polar space % (9) Take the FFT of (7) % (10) Take the FFT of (8) % (11) Compute phase correlation of (9) and (10) % (12) Find the location (x,y) in (11) of the peak of the phase correlation % (13) Compute angle (360 / Image Y Size) * y from (12) % (14) Rotate the image from (2) by - angle from (13) % (15) Rotate the image from (2) by - angle + 180 from (13) % (16) Take the FFT of (14) % (17) Take the FFT of (15) % (18) Compute phase correlation of (3) and (16) % (19) Compute phase correlation of (3) and (17) % (20) Find the location (x,y) in (18) of the peak of the phase correlation % (21) Find the location (x,y) in (19) of the peak of the phase correlation % (22) If phase peak in (20) > phase peak in (21), (y,x) from (20) is the translation % (23a) Else (y,x) from (21) is the translation and also: % (23b) If the angle from (13) < 180, add 180 to it, else subtract 180 from it. % (24) Tada! % Requires (ouch): % 6 x FFT % 4 x FFT Shift % 3 x IFFT % 2 x Log Polar % 3 x Phase Correlations % 2 x High Pass Filter % 2 x Image Rotation % --------------------------------------------------------------------- % Load first image (I1) % I1 = imread('lena.bmp'); % Load second image (I2) % I2 = imread('lena_cropped_shifted.bmp'); % Convert both to FFT, centering on zero frequency component SizeX = size(I1, 1); SizeY = size(I1, 2); FA = fftshift(fft2(I1)); FB = fftshift(fft2(I2)); % Output (FA, FB) % --------------------------------------------------------------------- % Convolve the magnitude of the FFT with a high pass filter) IA = hipass_filter(size(I1, 1),size(I1,2)).*abs(FA); IB = hipass_filter(size(I2, 1),size(I2,2)).*abs(FB); % Transform the high passed FFT phase to Log Polar space L1 = transformImage(IA, SizeX, SizeY, SizeX, SizeY, 'nearest', size(IA) / 2, 'valid'); L2 = transformImage(IB, SizeX, SizeY, SizeX, SizeY, 'nearest', size(IB) / 2, 'valid'); % Convert log polar magnitude spectrum to FFT THETA_F1 = fft2(L1); THETA_F2 = fft2(L2); % Compute cross power spectrum of F1 and F2 a1 = angle(THETA_F1); a2 = angle(THETA_F2); THETA_CROSS = exp(i * (a1 - a2)); THETA_PHASE = real(ifft2(THETA_CROSS)); % combImage = plant; for p=1:total_height for q=1:total_width if (combImage(p,q)==0) combImage(p,q) = bleed(p,q); end end end % Show final image % imshow(combImage, [0 255]); % ---------------------------------------------------------------------% Performs Log Polar Transformfunction [r,g,b] = transformImage(A, Ar, Ac, Nrho, Ntheta, Method, Center, Shape)% Inputs: A the input image% Nrho the desired number of rows of transformed image% Ntheta the desired number of columns of transformed image% Method interpolation method (nearest,bilinear,bicubic)% Center origin of input image% Shape output size (full,valid)% Class storage class of Aglobal rho;theta = linspace(0,2*pi,Ntheta+1); theta(end) = [];switch Shapecase 'full' corners = [1 1;Ar 1;Ar Ac;1 Ac]; d = max(sqrt(sum((repmat(Center(:)',4,1)-corners).^2,2)));case 'valid' d = min([Ac-Center(1) Center(1)-1 Ar-Center(2) Center(2)-1]);endminScale = 1;rho = logspace(log10(minScale),log10(d),Nrho)'; % default 'base 10' logspace - play with d to change the scale of the log axis% convert polar coordinates to cartesian coordinates and centerxx = rho*cos(theta) + Center(1);yy = rho*sin(theta) + Center(2);if nargout==3 if strcmp(Method,'nearest'), % Nearest neighbor interpolation r=interp2(A(:,:,1),xx,yy,'nearest'); g=interp2(A(:,:,2),xx,yy,'nearest'); b=interp2(A(:,:,3),xx,yy,'nearest'); elseif strcmp(Method,'bilinear'), % Linear interpolation r=interp2(A(:,:,1),xx,yy,'linear'); g=interp2(A(:,:,2),xx,yy,'linear'); b=interp2(A(:,:,3),xx,yy,'linear'); elseif strcmp(Method,'bicubic'), % Cubic interpolation r=interp2(A(:,:,1),xx,yy,'cubic'); g=interp2(A(:,:,2),xx,yy,'cubic'); b=interp2(A(:,:,3),xx,yy,'cubic'); else error(['Unknown interpolation method: ',method]); end % any pixels outside , pad with black mask= (xx>Ac) | (xx<1) | (yy>Ar) | (yy<1); r(mask)=0; g(mask)=0; b(mask)=0;else if strcmp(Method,'nearest'), % Nearest neighbor interpolation r=interp2(A,xx,yy,'nearest'); elseif strcmp(Method,'bilinear'), % Linear interpolation r=interp2(A,xx,yy,'linear'); elseif strcmp(Method,'bicubic'), % Cubic interpolation r=interp2(A,xx,yy,'cubic'); else error(['Unknown interpolation method: ',method]); end % any pixels outside warp, pad with black mask= (xx>Ac) | (xx<1) | (yy>Ar) | (yy<1); r(mask)=0;end % ---------------------------------------------------------------------% Returns high-pass filterfunction H = hipass_filter(ht,wd)% hi-pass filter function% ...designed for use with Fourier-Mellin stuffres_ht = 1 / (ht-1);res_wd = 1 / (wd-1);eta = cos(pi*(-0.5:res_ht:0.5));neta = cos(pi*(-0.5:res_wd:0.5));X = eta'*neta;H=(1.0-X).*(2.0-X);
3 仿真结果
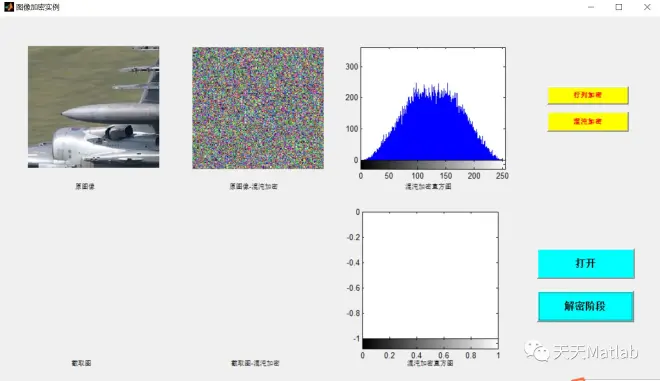
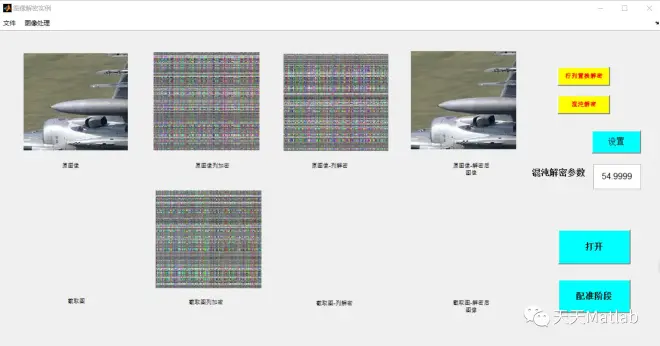
4 参考文献
【图像加密】基于正交拉丁方置乱+混沌图像加密解密含Matlab源码
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。


