【转】张量处理单元
张量处理单元
张量处理单元
张量处理单元( TPU )是专用集成电路( ASIC ),它实现了针对计算要求而优化的硬件电路深度神经网络。 TPU 基于复杂指令集计算机( CISC )指令集,该指令集实现用于训练深度神经网络的复杂任务的高级指令。 TPU 架构的核心在于优化矩阵运算的脉动数组。

The Architecture of TPUImage from: https://cloud.google.com/blog/big-data/2017/05/images/149454602921110/tpu-15.png
TensorFlow 提供了一个编译器和软件堆栈,可将 API 调用从 TensorFlow 图转换为 TPU 指令。以下框图描述了在 TPU 堆栈顶部运行的 TensorFlow 模型的体系结构:

Image from: https://cloud.google.com/blog/big-data/2017/05/images/149454602921110/tpu-2.pngFor more information on the TPU architecture, read the blog at the following link: https://cloud.google.com/blog/big-data/2017/05/an-in-depth-look-at-googles-first-tensor-processing-unit-tpu.
TPU 的 TensorFlow API 位于tf.contrib.tpu模块中。为了在 TPU 上构建模型,使用以下三个 TPU 特定的 TensorFlow 模块:
tpu_config:tpu_config模块允许您创建配置对象,其中包含有关将运行模型的主机的信息。tpu_estimator:tpu_estimator模块将估计器封装在[HTG2]类中。要在 TPU 上运行估计器,我们创建此类的对象。tpu_optimizer:tpu_optimizer模块包装优化器。例如,在下面的示例代码中,我们将tpu_optimizer类中的 SGD 优化器包装在tpu_optimizer类中。
例如,以下代码使用 TF Estimator API 为 TPU 上的 MNIST 数据集构建 CNN 模型:
以下代码改编自 https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu-demos/blob/master/cloud_tpu/models/mnist/mnist.py.
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.tpu.python.tpu import tpu_config
from tensorflow.contrib.tpu.python.tpu import tpu_estimator
from tensorflow.contrib.tpu.python.tpu import tpu_optimizer
learning_rate = 0.01
batch_size = 128
def metric_fn(labels, logits):
predictions = tf.argmax(logits, 1)
return {
"accuracy": tf.metrics.precision(
labels=labels, predictions=predictions),
}
def model_fn(features, labels, mode):
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT:
raise RuntimeError("mode {} is not supported yet".format(mode))
input_layer = tf.reshape(features, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=input_layer,
filters=32,
kernel_size=[5, 5],
padding="same",
activation=tf.nn.relu)
pool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv1, pool_size=[2, 2],
strides=2)
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=pool1,
filters=64,
kernel_size=[5, 5],
padding="same",
activation=tf.nn.relu)
pool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv2, pool_size=[2, 2],
strides=2)
pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
dense = tf.layers.dense(inputs=pool2_flat, units=128,
activation=tf.nn.relu)
dropout = tf.layers.dropout(
inputs=dense, rate=0.4,
training=mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN)
logits = tf.layers.dense(inputs=dropout, units=10)
onehot_labels = tf.one_hot(indices=tf.cast(labels, tf.int32), depth=10)
loss = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(
onehot_labels=onehot_labels, logits=logits)
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL:
return tpu_estimator.TPUEstimatorSpec(
mode=mode,
loss=loss,
eval_metrics=(metric_fn, [labels, logits]))
# Train.
decaying_learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate,
tf.train.get_global_step(),
100000,0.96)
optimizer = tpu_optimizer.CrossShardOptimizer(
tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(
learning_rate=decaying_learning_rate))
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss,
global_step=tf.train.get_global_step())
return tpu_estimator.TPUEstimatorSpec(mode=mode,
loss=loss, train_op=train_op)
def get_input_fn(filename):
def input_fn(params):
batch_size = params["batch_size"]
def parser(serialized_example):
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
"image_raw": tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
"label": tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
})
image = tf.decode_raw(features["image_raw"], tf.uint8)
image.set_shape([28 * 28])
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32) * (1\. / 255) - 0.5
label = tf.cast(features["label"], tf.int32)
return image, label
dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(
filename, buffer_size=FLAGS.dataset_reader_buffer_size)
dataset = dataset.map(parser).cache().repeat()
dataset = dataset.apply(
tf.contrib.data.batch_and_drop_remainder(batch_size))
images, labels = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator().get_next()
return images, labels
return input_fn
# TPU config
master = 'local' #URL of the TPU instance
model_dir = '/home/armando/models/mnist'
n_iterations = 50 # number of iterations per TPU training loop
n_shards = 8 # number of TPU chips
run_config = tpu_config.RunConfig(
master=master,
evaluation_master=master,
model_dir=model_dir,
session_config=tf.ConfigProto(
allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=True
),
tpu_config=tpu_config.TPUConfig(n_iterations,
n_shards
)
)
estimator = tpu_estimator.TPUEstimator(
model_fn=model_fn,
use_tpu=True,
train_batch_size=batch_size,
eval_batch_size=batch_size,
config=run_config)
train_file = '/home/armando/datasets/mnist/train' # input data file
train_steps = 1000 # number of steps to train for
estimator.train(input_fn=get_input_fn(train_file),
max_steps=train_steps
)
eval_file = '/home/armando/datasets/mnist/test' # test data file
eval_steps = 10
estimator.evaluate(input_fn=get_input_fn(eval_file),
steps=eval_steps
)
有关在 TPU 上构建模型的更多示例,请访问以下链接:https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu-demos.
优秀的 Verilog/FPGA开源项目介绍(二十)- 张量处理单元(TPU)

luoganttcc

于 2022-12-07 17:38:20 发布

849

收藏 14
分类专栏: 芯片 文章标签: fpga开发 开源
版权

开源项目管理文章已被社区收录
加入社区

芯片专栏收录该内容
134 篇文章10 订阅
订阅专栏
介绍
张量处理单元( Tensor Processing Unit, TPU ) 是谷歌专门为神经网络机器学习开发的人工智能加速器 专用集成电路(ASIC) ,特别是使用谷歌自己的TensorFlow软件。谷歌于 2015 年开始在内部使用 TPU,并于 2018 年将它们作为其云基础设施的一部分并通过提供较小版本的芯片出售给第三方使用。

张量处理单元于 2016 年 5 月在Google I/O上宣布:当时该公司表示 TPU 已经在其数据中心内使用了一年多。该芯片专为 Google 的TensorFlow框架设计,用于神经网络等机器学习应用。
与图形处理单元相比,它设计用于大量低精度计算(例如低至8 位精度) ,每焦耳有更多的输入/输出操作,无需用于光栅化/纹理映射的硬件。根据Norman Jouppi的说法, TPU ASIC安装在散热器组件中,该组件可以安装在数据中心机架内的硬盘驱动器插槽中。不同类型的处理器适合不同类型的机器学习模型,TPU 非常适合CNN而 GPU 对一些全连接的神经网络有长处,而 CPU 对RNN有长处。
经过几年的发展,TPU已经发布了四个版本,下面是其发展历程:
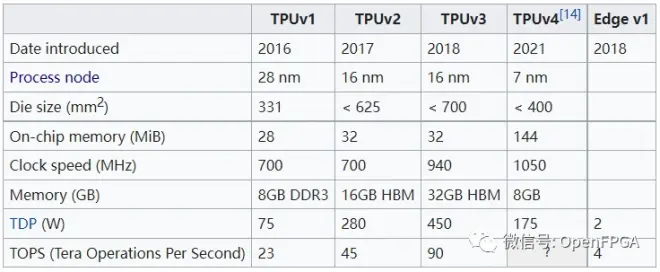
详细介绍:<【科普】什么是TPU?>
接下来介绍一些TPU项目。
tinyTPU
❝https://github.com/jofrfu/tinyTPU

该项目的目的是创建一个与谷歌的张量处理单元具有相似架构的机器学习协处理器。该实现的资源可定制,可以以不同的尺寸使用以适应每种类型的 FPGA。这允许在嵌入式系统和物联网设备中部署该协处理器,但也可以扩大规模以用于数据中心和高性能机器。AXI 接口允许以多种组合方式使用。对 Xilinx Zynq 7020 SoC 进行了评估。下面的链接中是使用vivado进行使用的一个DEMO:
❝https://github.com/jofrfu/tinyTPU/blob/master/getting_started.pdf
同时,该项目也是一片论文的验证项目,论文地址:
❝https://reposit.haw-hamburg.de/bitstream/20.500.12738/8527/1/thesis.pdf
性能
使用 MNIST 数据集训练的样本模型在不同大小的 MXU 上进行了评估,频率为 177.77 MHz,理论性能高达 72.18 GOPS。然后将实际时序测量与传统处理器进行比较:
177.77 MHz 的张量处理单元:
Matrix Width N
6
8
10
12
14
Instruction Count
431
326
261
216
186
Duration in us (N input vectors)
383
289
234
194
165
Duration per input vector in us
63
36
23
16
11
下面是其他处理器的对比结果:
Processor
Intel Core i5-5287U at 2.9 GHz
BCM2837 4x ARM Cortex-A53 at 1.2 GHz
Duration per input vector in us
62
763
Free-TPU
❝https://github.com/embedeep/Free-TPU

编译好的BOOTbin,因为TPU和引脚没关联,所以可以直接进行使用验证。
❝https://github.com/embedeep/Free-TPU-OS
描述
Free TPU是用于深度学习 EDGE 推理的商业 TPU 设计的免费版本,可以部署在任何 FPGA 设备上,包括 Xilinx Zynq-7020 或 Kintex7-160T(这两个都是生产的好选择)。实际上,不仅是 TPU 逻辑设计, Free TPU还包括支持所有 caffe 层的 EEP 加速框架,可以在任何 CPU 上运行(如 Zynq-7020 的 ARM A9 或 INTEL/AMD)。TPU 和 CPU 在深度学习推理框架的计划下相互协作(任何交替顺序)。
系统结构

对比


在用户看来,Free-TPU和EEP-TPU功能相同,但推理时间不同。
这是一个极其完整的项目,关于怎么运行,怎么调用都有很详细的步骤,这里就不再赘述了,更多详情,请访问:
❝https://www.embedeep.com
SimpleTPU
❝https://github.com/cea-wind/SimpleTPU

张量处理单元旨在加速矩阵乘法,特别是对于多层感知器和卷积神经网络。
此实现主要遵循 Google TPU Version 1,该架构在
❝https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1704/1704.04760.pdf
中有介绍。
主要特点
Simple TPU 的主要特性包括
Int8 乘法和 Int32 累加器
基于 VLIW 的并行指令
基于向量架构的数据并行
以下是 Simple TPU 可以支持的一些操作。
资源占用情况
虽然该工程比较完整,后续也有DEMO演示,但是该工程使用HLS制作的,详细信息可以查看下面的网址
❝https://www.cnblogs.com/sea-wind/p/10993958.html
tiny-tpu
❝https://github.com/cameronshinn/tiny-tpu
谷歌的TPU架构:
Tiny TPU是基于 FPGA 的 Google张量处理单元的小规模实现。该项目的目标是了解加速器设计从硬件到软件的端到端技术,同时破译谷歌专有技术的低层次复杂性。在此过程中,我们探索了小规模、低功耗 TPU 的可能性。
该项目在 Quartus 15.0 上综合并编程到 Altera DE1-SoC FPGA 上。
更多详细信息:
❝https://github.com/cameronshinn/tiny-tpu/blob/master/docs/report/report.pdf
TPU-Tensor-Processing-Unit
❝https://github.com/leo47007/TPU-Tensor-Processing-Unit
介绍
在有两个矩阵需要做矩阵乘法的场景下,矩阵A(选择权重矩阵)与矩阵B(选择矩阵)相,每一个一个都是 32x32。最后他们开始做每个矩阵的乘法,每个矩阵的因素将首先转换成一个顺序输入 TPU 中,输入其特定的矩阵,然后再将这些单元最多向连接的方向输入。在下一个周期中,每个单元将其权重和数据方向赋予下一个格。从左到右。
因为这个项目有中文的详细介绍,所以就不过多赘述了。
❝https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/26522315
Systolic-array-implementation-in-RTL-for-TPU
❝https://github.com/abdelazeem201/Systolic-array-implementation-in-RTL-for-TPU
如下图所示,在有两个矩阵需要做矩阵乘法的场景下,矩阵A(命名权重矩阵)与矩阵B(命名数据矩阵)相乘,每个矩阵为8x8。一旦他们开始做矩阵乘法,两个矩阵的这些系数将首先转换成一个顺序输入到 TPU 中,然后输入到每个特定的队列中。然后这些队列将最多向其连接的单元输出 8 个数据,这些单元将根据它接收到的权重和数据进行乘法和加法。并且在下一个周期中,每个单元格将其权重和数据转发给下一个单元格。权重从上到下,数据从左到右。
该项目虽然完成了相关的目的,但是只是完成了相关工作,实际使用时需要进行一些优化。
super_small_toy_tpu
❝https://github.com/dldldlfma/super_small_toy_tpu
如果说上面几个TPU比较复杂,那么这个就可以用“精简”来形容了。
整个代码非常精简,适合入门想研究TPU的人。
AIC2021-TPU
❝https://github.com/charley871103/TPU
❝https://github.com/Oscarkai9139/AIC2021-TPU
❝https://github.com/hsiehong/tpu
这个项目是AIC2021-TPU,类似的项目有很多,都是理论研究的项目,和上面的项目一样都是非常非常适合入门研究的人员,里面的理论都是极其详细的。
systolic-array
❝https://github.com/Dazhuzhu-github/systolic-array
verilog实现TPU中的脉动阵列计算卷积的module
data为实验数据
source为源码
testbench 测试各个模块用的testbench
data-preprocessing 原本是要写将卷积操作用python预先imtocol操作的,但后来直接使用matlab生成数据进行测试了
tpu_v2
❝https://github.com/UT-LCA/tpu_v2
项目没有多余的介绍,整个项目是基于Altera-DE3设计,EDA工具是Quartus II。
google-coral-baseboard
❝https://github.com/antmicro/google-coral-baseboard
NXP i.MX8X 和 Google 的 Edge TPU ML 推理 ASIC(也可作为Coral Edge TPU 开发板的一部分)的基板的开放硬件设计文件。该板提供标准 I/O 接口,并允许用户通过统一的柔性扁平电缆 (FFC) 连接器与两个兼容 MIPI CSI-2 的视频设备连接。
PCB 项目文件是在 Altium Designer 14.1 中准备的。
该项目是一个硬件方案,谷歌Coral Edge TPU的硬件验证方案。
neural-engine
❝https://github.com/hollance/neural-engine
大多数新的 iPhone 和 iPad 都有神经引擎,这是一种特殊的处理器,可以让机器学习模型变得非常快,但对于这种处理器的实际工作原理,公众知之甚少。
Apple 神经引擎(或 ANE)是NPU的一种,代表神经处理单元。它就像 GPU,但 NPU 不是加速图形,而是加速卷积和矩阵乘法等神经网络操作。
ANE 并不是唯一的 NPU——除了 Apple 之外,许多公司都在开发自己的 AI 加速器芯片。除了神经引擎,最著名的 NPU 是谷歌的 TPU(或 Tensor Processing Unit)。
这个项目并不是一个实现TPU的项目,但是是一个关于Apple 神经引擎(或 ANE)介绍及相关文档的集合的项目。
总结
今天介绍了几个TPU的项目,因为在国内TPU可能很多人都没有听说过,所以接下来我会出几篇文章介绍一下。同时这些项目前面几个非常完整,完全可以优化后进行商业推广(注意开源协议),最后几个项目是一些补充的知识,想要了解相关的知识的朋友可以查看一下。

