PoolFormer实战:使用PoolFormer实现图像分类任务(一)
摘要
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418
论文翻译:https://blog.csdn.net/hhhhhhhhhhwwwwwwwwww/article/details/128281326
官方源码:https://github.com/sail-sg/poolformer
模型代码解析:https://blog.csdn.net/hhhhhhhhhhwwwwwwwwww/article/details/128475827
完整的代码:https://download.csdn.net/download/hhhhhhhhhhwwwwwwwwww/87357450
MetaFormer是颜水成大佬的一篇Transformer的论文,该篇论文的贡献主要有两点:第一、将Transformer抽象为一个通用架构的MetaFormer,并通过经验证明MetaFormer架构在Transformer/ mlp类模型取得了极大的成功。
第二、通过仅采用简单的非参数算子pooling作为MetaFormer的极弱token混合器,构建了一个名为PoolFormer。
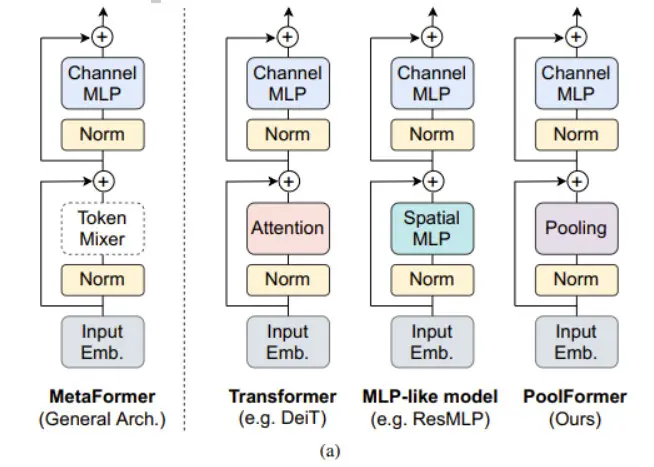
这篇文章主要讲解如何使用PoolFormer完成图像分类任务,接下来我们一起完成项目的实战。本例选用的模型是poolformer_s24,在植物幼苗数据集上实现了97%的准确率。
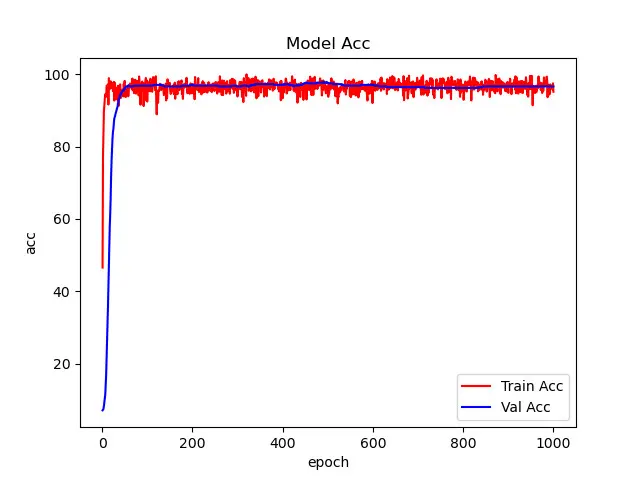
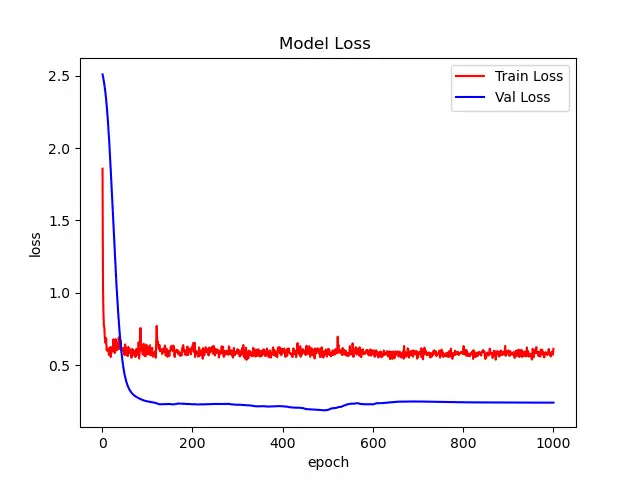
通过这篇文章能让你学到:
如何使用数据增强,包括transforms的增强、CutOut、MixUp、CutMix等增强手段?
如何实现PoolFormer模型实现训练?
如何使用pytorch自带混合精度?
如何使用梯度裁剪防止梯度爆炸?
如何使用DP多显卡训练?
如何绘制loss和acc曲线?
如何生成val的测评报告?
如何编写测试脚本测试测试集?
如何使用余弦退火策略调整学习率?
如何使用AverageMeter类统计ACC和loss等自定义变量?
如何理解和统计ACC1和ACC5?
如何使用EMA?
如果使用Grad-CAM 实现热力图可视化?
安装包
安装timm
使用pip就行,命令:
pip install timm
本文实战用的timm里面的模型。
安装 grad-cam
pip install grad-cam
数据增强Cutout和Mixup
为了提高成绩我在代码中加入Cutout和Mixup这两种增强方式。实现这两种增强需要安装torchtoolbox。安装命令:
pip install torchtoolbox
Cutout实现,在transforms中。
from torchtoolbox.transform import Cutout
# 数据预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
Cutout(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
])
需要导入包:from timm.data.mixup import Mixup,
定义Mixup,和SoftTargetCrossEntropy
mixup_fn = Mixup(
mixup_alpha=0.8, cutmix_alpha=1.0, cutmix_minmax=None,
prob=0.1, switch_prob=0.5, mode='batch',
label_smoothing=0.1, num_classes=12)
criterion_train = SoftTargetCrossEntropy()
参数详解:
★mixup_alpha (float): mixup alpha 值,如果 > 0,则 mixup 处于活动状态。
”
★ ”
★cutmix_alpha (float):cutmix alpha 值,如果 > 0,cutmix 处于活动状态。
”
★ ”
★cutmix_minmax (List[float]):cutmix 最小/最大图像比率,cutmix 处于活动状态,如果不是 None,则使用这个 vs alpha。
”
★ ”
★如果设置了 cutmix_minmax 则cutmix_alpha 默认为1.0
”
★ ”
★prob (float): 每批次或元素应用 mixup 或 cutmix 的概率。
”
★ ”
★switch_prob (float): 当两者都处于活动状态时切换cutmix 和mixup 的概率 。
”
★ ”
★mode (str): 如何应用 mixup/cutmix 参数(每个'batch','pair'(元素对),'elem'(元素)。
”
★ ”
★correct_lam (bool): 当 cutmix bbox 被图像边框剪裁时应用。 lambda 校正
”
★ ”
★label_smoothing (float):将标签平滑应用于混合目标张量。
”
★ ”
★num_classes (int): 目标的类数。
”
EMA
EMA(Exponential Moving Average)是指数移动平均值。在深度学习中的做法是保存历史的一份参数,在一定训练阶段后,拿历史的参数给目前学习的参数做一次平滑。具体实现如下:
import logging
from collections import OrderedDict
from copy import deepcopy
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
_logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class ModelEma:
def __init__(self, model, decay=0.9999, device='', resume=''):
# make a copy of the model for accumulating moving average of weights
self.ema = deepcopy(model)
self.ema.eval()
self.decay = decay
self.device = device # perform ema on different device from model if set
if device:
self.ema.to(device=device)
self.ema_has_module = hasattr(self.ema, 'module')
if resume:
self._load_checkpoint(resume)
for p in self.ema.parameters():
p.requires_grad_(False)
def _load_checkpoint(self, checkpoint_path):
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path, map_location='cpu')
assert isinstance(checkpoint, dict)
if 'state_dict_ema' in checkpoint:
new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
for k, v in checkpoint['state_dict_ema'].items():
# ema model may have been wrapped by DataParallel, and need module prefix
if self.ema_has_module:
name = 'module.' + k if not k.startswith('module') else k
else:
name = k
new_state_dict[name] = v
self.ema.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)
_logger.info("Loaded state_dict_ema")
else:
_logger.warning("Failed to find state_dict_ema, starting from loaded model weights")
def update(self, model):
# correct a mismatch in state dict keys
needs_module = hasattr(model, 'module') and not self.ema_has_module
with torch.no_grad():
msd = model.state_dict()
for k, ema_v in self.ema.state_dict().items():
if needs_module:
k = 'module.' + k
model_v = msd[k].detach()
if self.device:
model_v = model_v.to(device=self.device)
ema_v.copy_(ema_v * self.decay + (1. - self.decay) * model_v)
加入到模型中。
#初始化
if use_ema:
model_ema = ModelEma(
model_ft,
decay=model_ema_decay,
device='cpu',
resume=resume)
# 训练过程中,更新完参数后,同步update shadow weights
def train():
optimizer.step()
if model_ema is not None:
model_ema.update(model)
# 将model_ema传入验证函数中
val(model_ema.ema, DEVICE, test_loader)
针对没有预训练的模型,容易出现EMA不上分的情况,这点大家要注意啊!
项目结构
PoolFormer_Demo
├─data1
│ ├─Black-grass
│ ├─Charlock
│ ├─Cleavers
│ ├─Common Chickweed
│ ├─Common wheat
│ ├─Fat Hen
│ ├─Loose Silky-bent
│ ├─Maize
│ ├─Scentless Mayweed
│ ├─Shepherds Purse
│ ├─Small-flowered Cranesbill
│ └─Sugar beet
├─mean_std.py
├─makedata.py
├─train.py
├─cam_image.py
└─test.py
mean_std.py:计算mean和std的值。
makedata.py:生成数据集。
ema.py:EMA脚本
train.py:训练PoolFormer模型
cam_image.py:热力图可视化
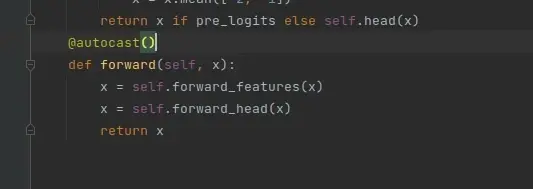
为了能在DP方式中使用混合精度,还需要在模型的forward函数前增加@autocast(),如果使用GPU训练导入包from torch.cuda.amp import autocast,如果使用CPU,则导入from torch.cpu.amp import autocast。
计算mean和std
为了使模型更加快速的收敛,我们需要计算出mean和std的值,新建mean_std.py,插入代码:
from torchvision.datasets import ImageFolder
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
def get_mean_and_std(train_data):
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_data, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=0,
pin_memory=True)
mean = torch.zeros(3)
std = torch.zeros(3)
for X, _ in train_loader:
for d in range(3):
mean[d] += X[:, d, :, :].mean()
std[d] += X[:, d, :, :].std()
mean.div_(len(train_data))
std.div_(len(train_data))
return list(mean.numpy()), list(std.numpy())
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_dataset = ImageFolder(root=r'data1', transform=transforms.ToTensor())
print(get_mean_and_std(train_dataset))
数据集结构:
运行结果:
([0.3281186, 0.28937867, 0.20702125], [0.09407319, 0.09732835, 0.106712654])
把这个结果记录下来,后面要用!
生成数据集
我们整理还的图像分类的数据集结构是这样的
data
├─Black-grass
├─Charlock
├─Cleavers
├─Common Chickweed
├─Common wheat
├─Fat Hen
├─Loose Silky-bent
├─Maize
├─Scentless Mayweed
├─Shepherds Purse
├─Small-flowered Cranesbill
└─Sugar beet
pytorch和keras默认加载方式是ImageNet数据集格式,格式是
├─data
│ ├─val
│ │ ├─Black-grass
│ │ ├─Charlock
│ │ ├─Cleavers
│ │ ├─Common Chickweed
│ │ ├─Common wheat
│ │ ├─Fat Hen
│ │ ├─Loose Silky-bent
│ │ ├─Maize
│ │ ├─Scentless Mayweed
│ │ ├─Shepherds Purse
│ │ ├─Small-flowered Cranesbill
│ │ └─Sugar beet
│ └─train
│ ├─Black-grass
│ ├─Charlock
│ ├─Cleavers
│ ├─Common Chickweed
│ ├─Common wheat
│ ├─Fat Hen
│ ├─Loose Silky-bent
│ ├─Maize
│ ├─Scentless Mayweed
│ ├─Shepherds Purse
│ ├─Small-flowered Cranesbill
│ └─Sugar beet
新增格式转化脚本makedata.py,插入代码:
import glob
import os
import shutil
image_list=glob.glob('data1/*/*.png')
print(image_list)
file_dir='data'
if os.path.exists(file_dir):
print('true')
#os.rmdir(file_dir)
shutil.rmtree(file_dir)#删除再建立
os.makedirs(file_dir)
else:
os.makedirs(file_dir)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
trainval_files, val_files = train_test_split(image_list, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
train_dir='train'
val_dir='val'
train_root=os.path.join(file_dir,train_dir)
val_root=os.path.join(file_dir,val_dir)
for file in trainval_files:
file_class=file.replace("\\","/").split('/')[-2]
file_name=file.replace("\\","/").split('/')[-1]
file_class=os.path.join(train_root,file_class)
if not os.path.isdir(file_class):
os.makedirs(file_class)
shutil.copy(file, file_class + '/' + file_name)
for file in val_files:
file_class=file.replace("\\","/").split('/')[-2]
file_name=file.replace("\\","/").split('/')[-1]
file_class=os.path.join(val_root,file_class)
if not os.path.isdir(file_class):
os.makedirs(file_class)
shutil.copy(file, file_class + '/' + file_name)
完成上面的内容就可以开启训练和测试了。

