R语言曲线回归:多项式回归、多项式样条回归、非线性回归数据分析
原文链接:http://tecdat.cn/?p=9508
本文将使用三种方法使模型适合曲线数据:1)多项式回归;2)用多项式样条进行B样条回归;3) 进行非线性回归。在此示例中,这三个中的每一个都将找到基本相同的最佳拟合曲线。
多项式回归
多项式回归实际上只是多元回归的一种特殊情况。
对于线性模型(lm),调整后的R平方包含在summary(model)语句的输出中。AIC是通过其自己的函数调用AIC(model)生成的。使用将方差分析函数应用于两个模型进行额外的平方和检验。
对于AIC,越小越好。对于调整后的R平方,越大越好。将模型a与模型b进行比较的额外平方和检验的非显着p值表明,带有额外项的模型与缩小模型相比,并未显着减少平方误差和。也就是说,p值不显着表明带有附加项的模型并不比简化模型好。
Data = read.table(textConnection(Input),header=TRUE)### Change Length from integer to numeric variable### otherwise, we will get an integer overflow error on big numbersData$Length = as.numeric(Data$Length)### Create quadratic, cubic, quartic variableslibrary(dplyr)Data =mutate(Data,Length2 = Length*Length,Length3 = Length*Length*Length,Length4 = Length*Length*Length*Length)library(FSA)headtail(Data)Length Clutch Length2 Length3 Length41 284 3 80656 22906304 65053903362 290 2 84100 24389000 70728100003 290 7 84100 24389000 707281000016 323 13 104329 33698267 1088454024117 334 2 111556 37259704 1244474113618 334 8 111556 37259704 12444741136
定义要比较的模型
model.1 = lm (Clutch ~ Length, data=Data)model.2 = lm (Clutch ~ Length + Length2, data=Data)model.3 = lm (Clutch ~ Length + Length2 + Length3, data=Data)model.4 = lm (Clutch ~ Length + Length2 + Length3 + Length4, data=Data)
生成这些模型的模型选择标准统计信息
summary(model.1)Coefficients:Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)(Intercept) -0.4353 17.3499 -0.03 0.98Length 0.0276 0.0563 0.49 0.63Multiple R-squared: 0.0148, Adjusted R-squared: -0.0468F-statistic: 0.24 on 1 and 16 DF, p-value: 0.631AIC(model.1)[1] 99.133summary(model.2)Coefficients:Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)(Intercept) -9.00e+02 2.70e+02 -3.33 0.0046 **Length 5.86e+00 1.75e+00 3.35 0.0044 **Length2 -9.42e-03 2.83e-03 -3.33 0.0045 **Multiple R-squared: 0.434, Adjusted R-squared: 0.358F-statistic: 5.75 on 2 and 15 DF, p-value: 0.014AIC(model.2)[1] 91.16157anova(model.1, model.2)Analysis of Variance TableRes.Df RSS Df Sum of Sq F Pr(>F)1 16 186.152 15 106.97 1 79.178 11.102 0.00455 **
其余模型继续此过程
四个多项式模型的模型选择标准。模型2的AIC最低,表明对于这些数据,它是此列表中的最佳模型。同样,模型2显示了最大的调整后R平方。最后,额外的SS测试显示模型2优于模型1,但模型3并不优于模型2。所有这些证据表明选择了模型2。
模型
AIC
调整后的R平方
p值
1
99.1
-0.047
2
91.2
0.36
0.0045
3
92.7
0.33
0.55
4
94.4
0.29
0.64
对比与方差分析
AIC,AICc或BIC中的任何一个都可以最小化以选择最佳模型。
$Fit.criteriaRank Df.res AIC AICc BIC R.squared Adj.R.sq p.value Shapiro.W Shapiro.p1 2 16 99.13 100.80 101.80 0.01478 -0.0468 0.63080 0.9559 0.52532 3 15 91.16 94.24 94.72 0.43380 0.3583 0.01403 0.9605 0.61163 4 14 92.68 97.68 97.14 0.44860 0.3305 0.03496 0.9762 0.90254 5 13 94.37 102.00 99.71 0.45810 0.2914 0.07413 0.9797 0.9474Res.Df RSS Df Sum of Sq F Pr(>F)1 16 186.152 15 106.97 1 79.178 10.0535 0.007372 ** ## Compares m.2 to m.13 14 104.18 1 2.797 0.3551 0.561448 ## Compares m.3 to m.24 13 102.38 1 1.792 0.2276 0.641254 ## Compares m.4 to m.3
研究最终模型
Coefficients:Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)(Intercept) -9.00e+02 2.70e+02 -3.33 0.0046 **Length 5.86e+00 1.75e+00 3.35 0.0044 **Length2 -9.42e-03 2.83e-03 -3.33 0.0045 **Multiple R-squared: 0.434, Adjusted R-squared: 0.358F-statistic: 5.75 on 2 and 15 DF, p-value: 0.014Anova Table (Type II tests)Response: ClutchSum Sq Df F value Pr(>F)Length 79.9 1 11.2 0.0044 **Length2 79.2 1 11.1 0.0045 **Residuals 107.0 15
模型的简单图解

检查模型的假设

线性模型中残差的直方图。这些残差的分布应近似正态。

残差与预测值的关系图。残差应无偏且均等。
###通过以下方式检查其他模型:
具有多项式样条的B样条回归
B样条回归使用线性或多项式回归的较小部分。它不假设变量之间存在线性关系,但是残差仍应是独立的。该模型可能会受到异常值的影响。
### --------------------------------------------------------------### B-spline regression, turtle carapace example### --------------------------------------------------------------summary(model) # Display p-value and R-squaredResidual standard error: 2.671 on 15 degrees of freedomMultiple R-squared: 0.4338, Adjusted R-squared: 0.3583F-statistic: 5.747 on 2 and 15 DF, p-value: 0.01403
模型的简单图解
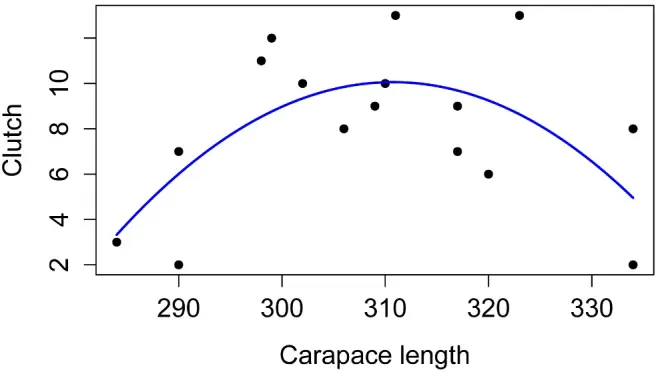
检查模型的假设

线性模型中残差的直方图。这些残差的分布应近似正态。
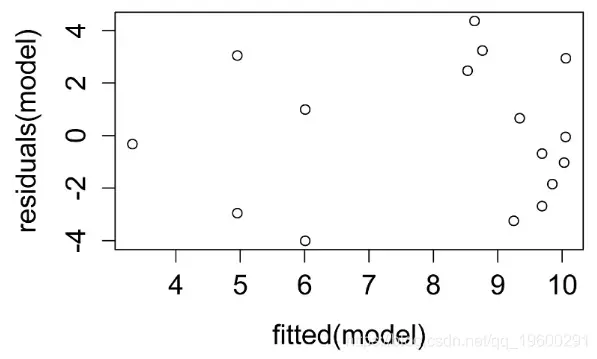
残差与预测值的关系图。残差应无偏且均等。
非线性回归
非线性回归可以将各种非线性模型拟合到数据集。这些模型可能包括指数模型,对数模型,衰减曲线或增长曲线。通过迭代过程,直到一定的收敛条件得到满足先后找到更好的参数估计。
在此示例中,我们假设要对数据拟合抛物线。
数据中包含变量(Clutch和Length),以及我们要估计的参数(Lcenter,Cmax和a)。
没有选择参数的初始估计的固定过程。通常,参数是有意义的。这里Lcenter 是顶点的x坐标,Cmax是顶点的y坐标。因此我们可以猜测出这些合理的值。 尽管我们知道参数a应该是负的,因为抛物线向下打开。
因为nls使用基于参数初始估计的迭代过程,所以如果估计值相差太远,它将无法找到解决方案,它可能会返回一组不太适合数据的参数估计。绘制解决方案并确保其合理很重要。
如果您希望模型具有整体p值,并且模型具有伪R平方,则需要将模型与null模型进行比较。从技术上讲,要使其有效,必须将null模型嵌套在拟合模型中。这意味着null模型是拟合模型的特例。
对于没有定义r平方的模型,已经开发了各种伪R平方值。
### --------------------------------------------------------------### Nonlinear regression, turtle carapace example### --------------------------------------------------------------Data = read.table(textConnection(Input),header=TRUE)Parameters:Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)Lcenter 310.72865 2.37976 130.57 < 2e-16 ***Cmax 10.05879 0.86359 11.65 6.5e-09 ***a -0.00942 0.00283 -3.33 0.0045 **
确定总体p值和伪R平方
anova(model, model.null)Res.Df Res.Sum Sq Df Sum Sq F value Pr(>F)1 15 106.972 17 188.94 -2 -81.971 5.747 0.01403 *$Pseudo.R.squared.for.model.vs.nullPseudo.R.squaredMcFadden 0.109631Cox and Snell (ML) 0.433836Nagelkerke (Cragg and Uhler) 0.436269
确定参数的置信区间
2.5 % 97.5 %Lcenter 305.6563154 315.800988774Cmax 8.2180886 11.899483768a -0.0154538 -0.003395949------Bootstrap statisticsEstimate Std. errorLcenter 311.07998936 2.872859816Cmax 10.13306941 0.764154661a -0.00938236 0.002599385------Median of bootstrap estimates and percentile confidence intervalsMedian 2.5% 97.5%Lcenter 310.770796703 306.78718266 316.153528168Cmax 10.157560932 8.58974408 11.583719723a -0.009402318 -0.01432593 -0.004265714
模型的简单图解

检查模型的假设

线性模型中残差的直方图。这些残差的分布应近似正态。
plot(fitted(model),residuals(model))

残差与预测值的关系图。残差无偏且均等。

