Lab Exercise 4
1. (简答题)
Students are required to submit your solutions before 0:00am on November 14th. You should only upload two files (do not zip), your notebook ".ipynb" file and PDF file generated after notebook execution.
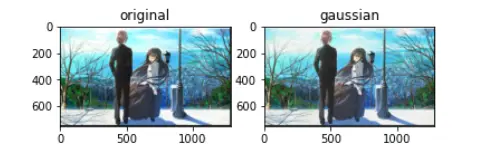
1. Add random noises to an image
1) Use skimage.util.random_noise (or other equivalent method functions) to add random noises
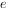
to any image, and display the resulting image.
2) Add random noises to the original image each time to generate a noisy image, repeat M times, accumulate all M noisy images, and then do average. which is
Show average pictures for M=50, 100, 150, 200 respectively.
3) What conclusions can you draw from the results?
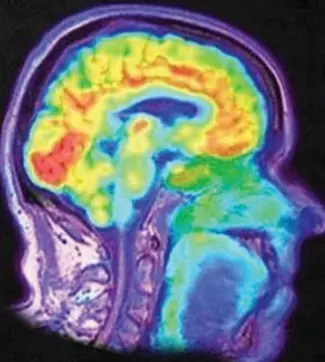
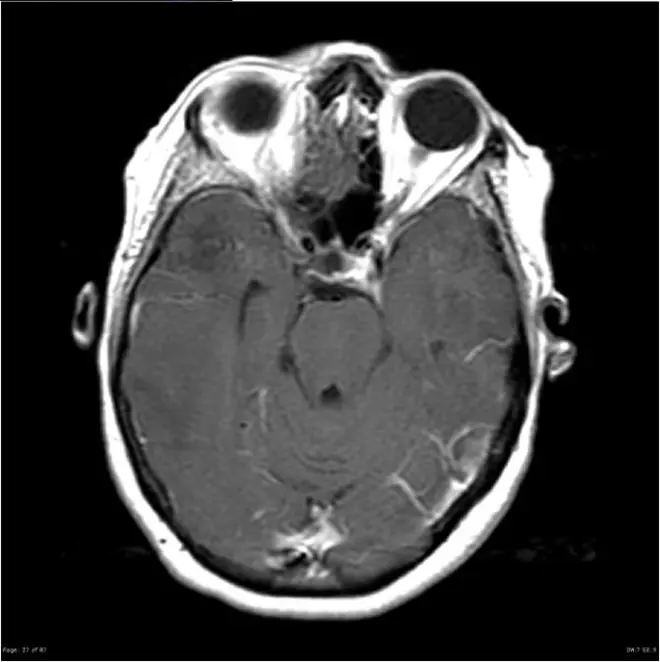
2. A ring-enhancing lesion is an abnormal radiologic sign on MRI or CT scans obtained using radiocontrast. On the image, there is an area of decreased density (see radiodensity) surrounded by a bright rim from concentration of the enhancing contrast dye. This enhancement may represent breakdown of the blood-brain barrier and the development of an inflammatory capsule. This can be a finding in numerous disease states. In the brain, it can occur with an early brain abscess as well as in Nocardia infections associated with lung cavitary lesions. In patients with HIV, the major differential is between CNS lymphoma and CNS toxoplasmosis, with CT imaging being the appropriate next step to differentiate between the two conditions.
The following is a head CT scan of a patient with a ring-enhanced lesion:
1) Design and implement a pseudocolor shading method to colorize head CT scans (grayscale images). The results can be similar to those shown in the example or other better methods (which can highlight the lesion area best).
2) Explain your pseudocolor shading method.
3) If you are required to segment the lesion area, what problems do you think you will encounter? Discuss how you would approach this problem? (Competent students may try to implement your idea, not asking for a perfect answer)
提供的图片:
作答:
import skimage
from skimage import util
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import CV2
import random
img = Image.open('image/original.png')
img = np.array(img)
noise_gs_img = util.random_noise(img,mode='gaussian')
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title('original')
plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title('gaussian')
plt.imshow(noise_gs_img)
plt.show()
Add random noises to the original image each time to generate a noisy image, repeat M times, accumulate all M noisy images, and then do average.
#展示图片函数
def show(img):
if img.ndim==2:
plt.imshow(img,cmap='gray')
else:
plt.imshow(CV2.cvtColor(img,CV2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
def gaussian_noise(image, count,mean=0.1, sigma=0.3):
"""
添加高斯噪声
:param image:原图
:param mean:均值
:param sigma:标准差 值越大,噪声越多
:return:噪声处理后的图片
"""
sum=0.000
image = np.asarray(image / 255, dtype=np.float32) # 图片灰度标准化
for i in range(count):
noise = np.random.normal(mean, sigma, image.shape).astype(dtype=np.float32) # 产生高斯噪声
sum=sum+noise
# print(sum)
noise=sum/(count*1.00)
# print(noise)
output = image + noise # 将噪声和图片叠加
output = np.clip(output, 0, 1)
output = np.uint8(output * 255)
return output
#50
image = CV2.imread("image/original.png")
out1 = gaussian_noise(image.copy(),50)
show(out1)

#100
out2= gaussian_noise(image.copy(),100)
show(out2)

#150
out3= gaussian_noise(image.copy(),150)
show(out3)

#200
out4= gaussian_noise(image.copy(),200)
show(out4)

1) Design and implement a pseudocolor shading method to colorize head CT scans (grayscale images). The results can be similar to those shown in the example or other better methods (which can highlight the lesion area best)
im_gray = CV2.imread("image/1.png", CV2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
im_color = CV2.applyColorMap(im_gray, CV2.COLORMAP_JET)
show(im_color)
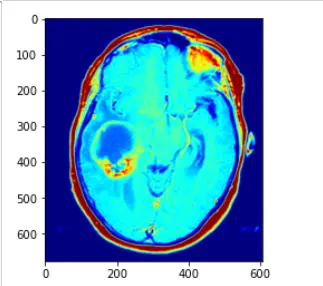
im_gray = CV2.imread("image/2.png", CV2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
im_color = CV2.applyColorMap(im_gray, CV2.COLORMAP_JET)
show(im_color)
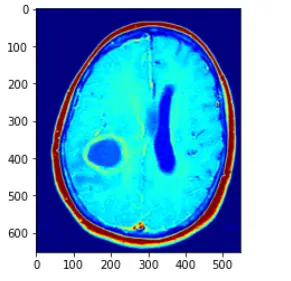
im_gray = CV2.imread("image/3.png", CV2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
im_color = CV2.applyColorMap(im_gray, CV2.COLORMAP_JET)
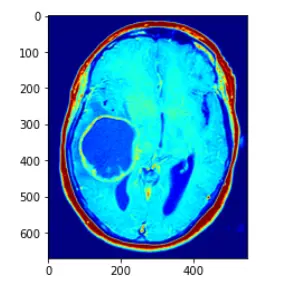
show(im_color)
im_gray = CV2.imread("image/10.png", CV2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
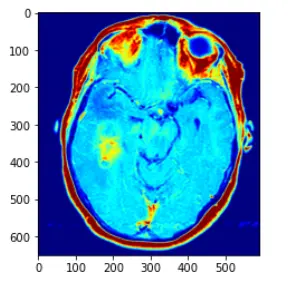
im_color = CV2.applyColorMap(im_gray, CV2.COLORMAP_JET)
show(im_color)
2) Explain your pseudocolor shading method.
解释如下:直接使用CV2.applyColorMap 方法,applyColorMap为伪彩色函数,建立在灰度图的前提下使用,CV2.COLORMAP_JET采用染色模式,灰度值越高则表现的颜色越为红色,灰度值越低的话,变现为蓝色
在此中间的灰度值渐变为蓝红之间的黄,绿等
而opencv中的applyColor函数其实现方法为对于遍历灰度图像获取每个像素点的灰度值,然后对灰度值进行层级划分,例如0~63 蓝色,64~127 紫色,128~191黄色,192~255红色
进行一个划分,然后对层级进行一个人,r,g,b的转化,设置相应的三通道值即可,转化为三通道图像,即可得到伪彩色图像处理的方法
3) If you are required to segment the lesion area, what problems do you think you will encounter? Discuss how you would approach this problem? (Competent students may try to implement your idea, not asking for a perfect answer)
我认为首先确定好哪里是受损伤的部位是一个问题,然后如何对受伤部位进行分割也是一个问题,我的话,在已知损伤部位的情况下,对ct图使用较深颜色笔进行边缘大致的画线圈画
然后用圈画之后,画出大致的轮廓,在伪彩色处理之后,损伤部位被清晰标注圈出来,这样子不就已经划分出来损伤和被损伤的部位了
(有些代码是百度的,csdn中的,毕竟不是造轮子,相互看看改改就能实现,但是如果想要真的了解学懂,还是慢慢看着来)

