我在B站上大学!【完整版-麻省理工-微积分重点】全18讲!学数学不看的微积分课程

P1-4 The big picture of Calculus
Calculus is about the connection between Function 1 and Function 2
- Function 1: Height y = f(t)
- Function 2: Slope S = y' = df/dt - the derivative of y
- Function 3: Bending B = y'' = d²f/dt² (d second f d t squared) - the second derivative of y
If we know y' and y'', we can find the max/min of the function 1
Max & Min
S = y', which is the derivative of y
- when y' = 0 , y = Max/Min;
- y' < 0 , y is going down;
- y' > 0 , y is going up.
B = y'', which is the second derivative of y
- when y'' = 0 , y = inflection point;
- y'' > 0 , y is a convex curve(bending up) , if y' = 0 and y'' > 0 , y = min;
- y'' < 0 , y is a concave curve(bending down) , if y' = 0 and y'' < 0 , y = max.
Some Important Functions of Calculus:
- y = x^n dy/dx = n*x^(n-1)
- y = sinx dy/dx = cosx
- y = e^x dy/dx = e^x
P5 The Exponential Function
the first differential equation: dy/dx = y
- when y = e^x, its slope is equal to itself - y' = dy/dx = e^x = y
- when y = c(e^x), dy/dx = c(e^x)
- the differential equation means an equation involves the function and its slope.
Base on this equation, we can prove (e^x)*(e^X) = e^(x+X)
- first step:
- reconstruction the function e^x that starts at e^0 = 1
- because n! will grow much faster than x^n, finally the number of (x^n)/n! will get extremely small and then the sum of this series comes to a limit

- second step: times two functions

Based on the reconstruction function:
- the number e is the sum of the exponential series when x = 1, rounded to 2.71828...

The graph of the function y = e^x

Example: computing compound interest

the second differential equation: dy/dx = cy
- when y = e^cx, dy/dx = y' = c(e^cx) = cy
P6 Integrals - from df/dt to f(t)
function 2 → function 1 : f(t) = ∫s(t)dt
Integral = function 1 = the area under the graph of function 2
P7 Limits and Continuous Functions
different types of limits:
an → A as n → ∞
- infinite limits (A = ∞)
- some positive number (A)
- zero(A = 0)
- ......
some special limits:
- an - bn → A - B = ∞ - ∞ (no answer, could be zero( an = bn = n), could be ∞( an = n^2 and bn = n), danger part in mathematics)
- an * bn → A * B = (0)*(∞)
- an/bn → A/B = 0/0 or ∞/∞
- (an)^bn → A^B = 0^0 or 1^ ∞
(1+1/n)^n → e
(1+1/(n^2))^n → 1
(1+1/n)^(n^2) → ∞
L'Hôpital's rule(洛必达法则)
If f(x) → 0 as x → 0, g(x) → 0 as x → 0,
f(x)/g(x) → △f/△g = (△f/△x)/(△g/△x) → slope(f)/slope(g)
exception:
f(x) = √x , the slope of f(x) is infinite, and the L rule doesn't work
when f(x) = √x at x = 0, slope not defined, but f(x) is continuous
if a function's got a slope that function's got to be continuous(可导必然连续,连续不一定可导(这里中英文字幕有点对不上))
Continuous:

if |x-a| < δ, then, |f(x)-f(a)| < ε
(当 x 落在a ± δ,f(x) 一定落在 f(a) ± ε)
P8 Derivatives of Sine and Cosine
To show d(sinx)/dx = cosx; d(cosx)/dx = -sinx:
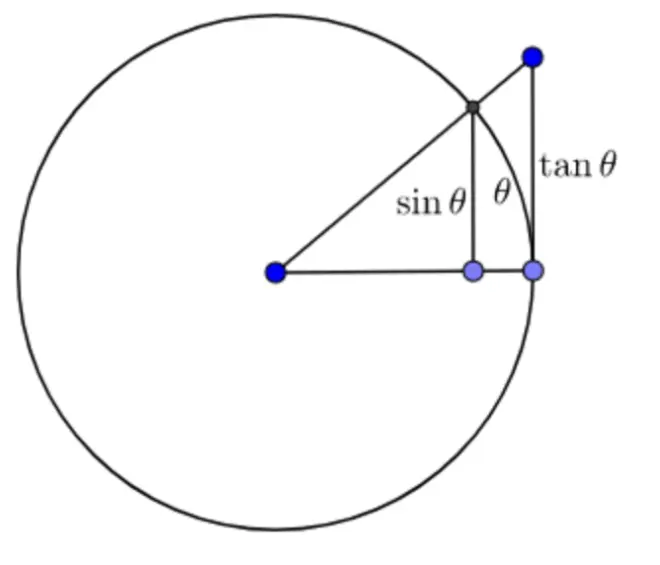
The first step: to show the limit of sinθ/θ → 1
sinθ < θ, θ > 0
∴ sinθ/θ < 1
tanθ > θ, 0 < θ < π/2
∴ tanθ = sinθ/cosθ > θ
∴ 1 > sinθ/θ > cosθ
prof. : maths always get some little trick
_ can't agree more!
∴ when θ → 0, sinθ/θ → 1

The second step: to show Δsinx/Δx → cosx, Δx → 0
sin(a+b) = sina*cosb + sinb*cosa

The third step: to show Δcosx/Δx → -sinx, Δx → 0
cos(a+b) = cosa*cosb - sina*sinb
Δcosx/Δx = (cos(x+Δx) - cosx)/Δx = (cosx*coxΔx - sinx*sinΔx-cosx)/Δx = cosx*(cosΔx - 1)/Δx - sinx*sinΔx/Δx
(cosΔx - 1)/Δx → 0

当x = 0, cosx = 1, y取得极大值,在该点的斜率是0,又可表示为 (cosΔx - 1)/(Δx - 0) = (cosΔx - 1)/Δx → 0
sinΔx/Δx → 1
∴ Δcosx/Δx → -sinx
P9 Product Rule and Quotient Rule
(一)Product Rule


ΔuΔv is negligible
∴ d(u*v) = uΔv + vΔu
∴ d(u*v)/dx = u*Δv/Δx + v*Δu/Δx = u*v' + v*u'
(二)Quotient Rule

P10 The Chain Rule

Discovery of chain rule
Δz/Δx = (Δz/Δy) * (Δy/Δx)
Example:
z' = -xe^(-(x^2)/2)
z'' = -x(-xe^(-(x^2)/2)) - e^(-(x^2)/2) = (x^2 - 1)e^(-(x^2)/2)
P11 Inverse functions and x = lny
y = f(x) and x = f⁻¹(x)
The function that have an inverse function have to be one-to-one: one x for one y, one y for one x
f(x) = y = e^x
f⁻¹(x) = x = lny - the natural logarithm
***x is the exponent, so the logarithm is the exponent in the original funciton

Key facts of logarithm
1- ln(y*Y) = lny + lnY
y = e^x and x = lny
Y = e^X and X = lnY
y*Y = (e^x)(e^X) = e^(x+X)
ln(y*Y) = lne^(x+X) = x + X = lny +lnY
2- ln(y^n) = n*lny
P12 Derivative of lny and sin⁻¹y
y = e^x and x = lny
To show d(lny)/dy = 1/y
ln(e^x) = x
(ln(e^x))' = 1
= (lny)' * e^x - chain rule
∴ (lny)' = 1/(e^x)
y = e^x
∴ (lny)' = 1/y
y = sinx and x = sin⁻¹y
y = sin(sin⁻¹y)
y' = 1 = cos(sin⁻¹y) * (d(sin⁻¹y)/dy)

x = θ
= cosθ * (d(sin⁻¹y)/dy)
= √(1-y^2) * (d(sin⁻¹y)/dy)
∴ d(sin⁻¹y)/dy = 1/√(1-y^2)
the derivative of cos⁻¹y = -1/√(1-y^2)
d(sin⁻¹y)/dy + d(cos⁻¹y)/dy = 0
∴ sin⁻¹y + cos⁻¹y = a costant = π/2
(sin⁻¹y = θ, cos⁻¹y = α, θ + α = 90˚)
P13 Growth rates and log graphs
(本节主要举例讲解log的实际应用:能够更精确地测量出函数中的指数大小(增长率))
Growth functions:
- linear growth(proportional to x = cx)
- polynomial growth(some power of x, like x^2, x^3...)
- exponential growth(2^x, e^x, 10^x...)
- factorial growth(x!, x^x...)
Decay functions:
1/x, 1/x^2, 1/e^x, 1/x!...
Some practical uses of log scale
example1:
example2:
P14 Two different ways that the derivatives are used
Linear Approximation
- Find f(x)
At x = a, df/dx = f'(a) ≈ (f(x) - f(a))/(x - a)
f(x) ≈ f(a) + (x - a)f'(a)
Example:
find√9.06
- find f(x), when x = 9.06

find e^0.01
f(x) = e^x, f'(x) = e^x
a = 0, f(a) = 1, f'(a) = 1
e^0.01 ≈ 1 + (0.01 - 0)*1 = 1.01
(f(a) + (x - a)f'(a) + ...不断逼近f(x), 下一项是(1/2)(x-a)^2*f''(a))
Newtone's Method
- Solve F(x) = 0 (find x)
At x = a, df/dx = F'(a) ≈ (F(x) - F(a))/(x - a)
x - a ≈ -F(a)/F'(a)
Example:
find√9.06
- when x = √9.06, x^2 - 9.06 = 0 = F(x)
F(x) = x^2 - 9.06 = 0, F'(x) = 2x
choose a = 3, F(a) = 3^2 - 9.06 = -0.06, F'(a) = 2*3 = 6
x - 3 ≈ 0.06/6 = 0.01, x ≈ 3.01
the 2nd cycle of newton's method - closer to the the x(solution)
choose A = 3.01, F(A) = 3.01^2 - 9.06 = 0.0001, F'(A) = 2A = 6.02
x(new) - 3.01 = -0.0001/6.02 = 3.009983...
x(new)^2 = 9.060000001 - extremely close to the x(solution)
P15 Power Series and Euler's Great Formula
Taylor series
Construct the power series:
f(x) = a0 + a1x + a2x^2 +a3x^3 + ... + anx^n
find an = ?, match at x = 0, anx^n = nth derivative of f(0)
- f(0), f'(0), f''(0), f'''(0), ..., nth derivative of f(0)
- nth derivative of nx^n = n!
e^x = 1 + x + (1/2)x^2 + (1/6)x^3 + ... + (1/n!)x^n
- match at x = 0, (e^0)''' = (e^0)'' = (e^0)' = e^0 = 1
f(x) = sinx = x - (1/3!)x^3 + (1/5!)x^5 - (1/7!)x^7 + ...
- f(x) = sinx, f'(x) = cosx, f''(x) = -sinx, f'''(x) = -cosx, f''''(x) = sinx, ...
- match x = 0, f'(0) = 1, f''(0) = 0, f'''(0) = -1, f''''(0) = 0, ...
- f(x) = a0 + a1x + a2x^2 +a3x^3 + ... + anx^n
- a0 = 0
- (a1x)' = f'(0) = 1, a1 = 1
- (a2x^2)'' = f''(0) = 0, a2 = 0
- (a3x^3)''' = f'''(0) = -1, a3 = -1/6
f(x) = cosx = 1 - (1/2!)x^2 + (1/4!)x^4 - ... (even power)
Euler's Great Formula

geometric series: 1/(1-x) = 1 + x + x^2 + x^3 + ..., |x| < 1
f(x) = 1/(1-x), f' = 1/(1-x)^2, f'' = 2/(1-x)^3,f''' = 3!/(1-x)^4
nth derivative of f(x) = n!/(1-x)^(n+1)
nth derivative of f(0) = n!
a0 = 1
(a1x)' = 1, a1 = 1
(a2x^2)' = 2a2x = f''(0) = 2, a2 = 1...
∴1/(1-x) = 1 + x + x^2 + x^3 + ...
∫(1/(1-x)) = -ln(1-x)= x + (1/2)x^2 + (1/3)x^3 +..., |x| < 0
P16 Differential Equations of Motion(eg. spring)

Example:
1、r = 0, F = ma
2、my'' + 2ry' + ky = 0
try y = e^λt , mλ^2 +2rλ + k = 0, λ = ( - r ± √(r^2-km))/m
(1)1y'' + 6y' +8y = 0, y = Ce^(-2t) + De^(-4t)
(2)1y'' + 6' + 10y = 0, y = Ae^(-3t)cost + Be^(-3t)isint
(3)1y'' + 6y' + 9y = 0, y = Ce^(-3t) + Dte^(-3t)
Conclusion:
P17 Differential Equations of Growth
dy/dt = Cy + S
P18 Summary
6 functions
- (x^(n+1)/n+1- x^n - n*x^(n-1)
- -cosx - sinx - cosx
- cosx - -sinx
- (e^cx)/c - e^cx - c*e^cx
- xlnx -x - lnx - 1/x
- δ function
6 rules
- af(x) + bg(x) - af' + bg'
- f(x)g(x) - f(x)*g' + g(x)*f'
- f(x)/g(x) - (g(x)*f' - f(x)*g')/(g(x)^2)
- x = f⁻¹(y) - dx/dy = 1/dy/dx
- chain rule = f(g(x)) - (df/dy)*(dy/dx)
- L' rule
6 Theorems

what are these mathematical symbols called in English
- f(t) is called "f of t", t is an input, f(t) is an output
- x^2 is called "x squared"
- e^x is called "e to the x", e^0.01: "e to the power point o one"
- n!= n factorial
- e is called Euler's number
- if a function is symmetric across 0: f(x) = f(-x), it is called an even function
- if a function is anti-symmetric across 0, it is called an odd function
- cos⁻¹ is called arc-cosine
Math glossary
calculus 微积分
function 函数
slope 斜率
algebra 代数
differential calculus - from f(t) to df/dt 微分学
integral calculus - from df/dt to f(t) 积分学
formula 公式
parabola 抛物线
derivative 导数(金融衍生品)
the second derivative 二阶导数
convex and concave curves 凸函数和凹函数
inflection point 拐点
cubic/quadratic/linear 三次方/二次方/直线
exponential equation 指数方程
factorial 阶乘
binomial theorem 二项式定理
geometric series/ progression: 1+x+x^2+x^3+...+x^n 几何级数:当x<1,几何级数趋向收敛;当x >=1,几何级数趋向 ∞
least squares 最小二乘法
trapezoid 梯形
square root 根号
epsilon = ε
delta = δ
radian 弧度
fraction 分数
symmetric 对称的
logarithm 对数
proportional to x = cx

