网联驾驶下能量管理系统对比研究: 协同跟车案例
A comparative study of energy management systems under connected driving: cooperative car-following case
Ozan Yazar, Serdar Coskun, Fengqi Zhang, Lin Li
In this work, we propose connected energy management systems for a cooperative hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) platoon. To this end, cooperative driving scenarios are established under different car-following behavior models using connected and automated vehicles technology, leading to a cooperative cruise control system (CACC) that explores the energy-saving potentials of HEVs. As a real-time energy management control, an equivalent consumption minimization strategy (ECMS) is utilized, wherein global energy-saving is achieved to promote environment-friendly mobility. The HEVs cooperatively communicate and exchange state information and control decisions with each other by sixth-generation vehicle-to-everything (6G-V2X) communications. In this study, three different car-following behavior models are used: intelligent driver model (IDM), Gazis–Herman–Rothery (GHR) model, and optimal velocity model (OVM). Adopting cooperative driving of six Toyota Prius HEV platoon scenarios, simulations under New European Driving Cycle (NEDC), Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicle Test Procedure (WLTP), and Highway Fuel Economy Test (HWFET), as well as human-in-the-loop (HIL) experiments, are carried out via MATLAB/Simulink/dSPACE for cooperative HEV platooning control via different car-following-linked-vehicle scenarios. The CACC-ECMS scheme is assessed for HEV energy management via 6G-V2X broadcasting, and it is found that the proposed strategy exhibits improvements in vehicular driving performance. The IDM-based CACC-ECMS is an energy-efficient strategy for the platoon that saves: (i) 8.29% fuel compared to the GHR-based CACC-ECMS and 10.47% fuel compared to the OVM-based CACC-ECMS under NEDC; (ii) 7.47% fuel compared to the GHR-based CACC-ECMS and 11% fuel compared to the OVM-based CACC-ECMS under WLTP; (iii) 3.62% fuel compared to the GHR-based CACC-ECMS and 4.22% fuel compared to the OVM-based CACC-ECMS under HWFET; and (iv) 11.05% fuel compared to the GHR-based CACC-ECMS and 18.26% fuel compared to the OVM-based CACC-ECMS under HIL.
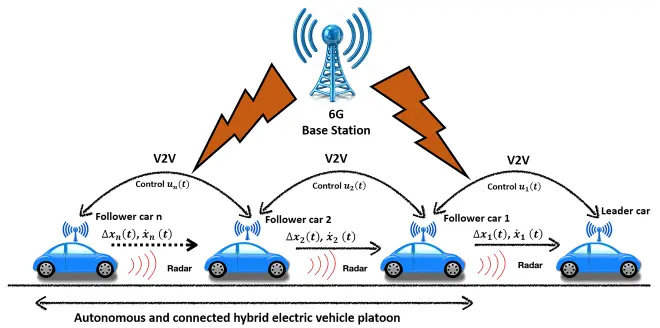
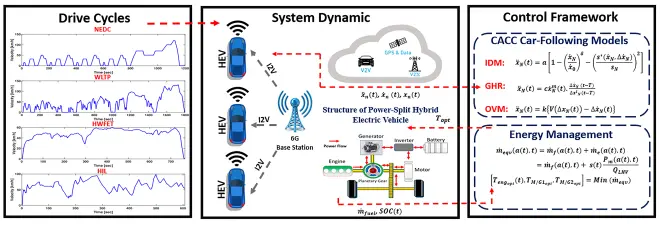

在这项工作中,作者提出了用于协作式混合动力电动汽车 (HEV) 排的互联能源管理系统。为此,利用互联和自动驾驶汽车技术,在不同的跟车行为模型下建立协同驾驶场景,从而开发出探索混合动力汽车节能潜力的协同巡航控制系统(CACC)。作为实时能源管理控制,采用等效消耗最小化策略(ECMS),实现全球节能,促进环保出行。HEV 通过第六代车联网 (6G-V2X) 通信相互协作通信和交换状态信息和控制决策。在这项研究中,使用了三种不同的跟车行为模型:智能驾驶员模型(IDM),Gazis-Herman-Rothery (GHR) 模型和最佳速度模型 (OVM)。采用丰田普锐斯HEV六排场景协同驾驶、新欧洲驾驶循环(NEDC)、全球统一轻型车辆测试程序(WLTP)和高速公路燃油经济性测试(HWFET)下的模拟,以及人在环(HIL) 实验是通过 MATLAB/Simulink/dSPACE 进行的,用于通过不同的跟驰链接车辆场景进行协作 HEV 队列控制。

