ES6中的类,模板字符串,Promise,拼接表格无序列表等等,回调地狱,ajax【诗书画唱】
内容索引:
1、通过ES6语法创建学生类(姓名,性别,班级)和游戏类(名称,公司,发行年份),添加各自的构造方法。
2、创建一个学生(姓名,性别,班级)数组,通过模板字符串拼接显示学生的所有信息(表格)
3、创建一个游戏数组(名称,公司,发行年份),通过模板字符串拼接显示游戏的所有信息(无序列表)
学习记录
示范例子
ES6Promise.html
ES6模板字符串.html
ES6中的类.html
回调地狱
ajax

1、通过ES6语法创建学生类(姓名,性别,班级)和游戏类(名称,公司,发行年份),添加各自的构造方法。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<script>
class Student{
constructor(n,s,a){
this.name = n;
this.sex = s;
this.age = a;
}
}
let s1= new Student('诗书画唱','男',20);
console.log(s1)
class Game{
constructor(n,c,y){
this.name = n;
this.company = c;
this.year =y;
}
}
let g1= new Game('诗书画唱游戏','诗书画唱游戏公司',2021);
console.log(g1)
</script>
<body>
</body>
</html>


2、创建一个学生(姓名,性别,班级)数组,通过模板字符串拼接显示学生的所有信息(表格)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
let studentArray = [{name:'诗书画唱1',sex:'男',banJi:'高三(6)班'},
{name:'诗书画唱2',sex:'男',banJi:'高三(7)班'},
{name:'诗书画唱3',sex:'男',banJi:'高三(8)班'}];
let html = `<tr><th>姓名</th><th>性别</th><th>班级</th></tr>`;
//下面的o就是数组中的object对象
for(let o of studentArray) {
html += `<tr>
<td> ${o.name}</td>
<td>${o.sex}</td>
<td>${o.banJi}</td>
</tr>`;
}
document.getElementById('tableId1').innerHTML = html;
}
</script>
<body>
<table id="tableId1" border="1">
</table>
</body>
</html>


3、创建一个游戏数组(名称,公司,发行年份),通过模板字符串拼接显示游戏的所有信息(无序列表)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
let gameArray = [{name:'诗书画唱游戏1',company:'诗书画唱游戏分公司1',year:2000},
{name:'诗书画唱游戏2',company:'诗书画唱游戏分公司2',year:2001},
{name:'诗书画唱游戏3',company:'诗书画唱游戏分公司3',year:2002}];
let html = ``;
for(let o of gameArray) {
html += `<ul>
<li> ${o.name}</li>
<li>${o.company}</li>
<li>${o.year}</li>
</ul>`;
}
document.getElementById('ulId1').innerHTML = html;
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="ulId1" border="1">
</div>
</body>
</html>



学习记录
越高级的语言,越接近于人类的语言,越好用,但是技术含量就越低
汇编语言
Promise内置对象。
Object,Date,Number,Array
promise:发誓,承诺
异步执行代码:几段代码同时执行。













示范例子
ES6Promise.html

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<script>
//Promise的构造方法中必须传入一个函数,当运行new Promise的时候,
//就会直接运行这个传入的函数
// let p = new Promise(function(){
// console.log('Hello world');
// });
//为了在需要的时候才创建Promise对象,将代码封装在一个函数中
function runAsync(){
return new Promise(function(){
console.log('Hello world');
});
}
//只有调用函数时才会创建Promise
let p = runAsync();
//回调地狱
// $.ajax({
// url: '',
// success: function(data){
// $.ajax({
// url: '?d=' + data,
// success: function(){
//
// }
// });
// }
// });
// setTimeout(function(){
// console.log('做完了第一道题');
// setTimeout(function(){
// console.log('做完了第二道题');
// setTimeout(function(){
// console.log('做完了第三道题')
// },3000);
// },3000);
// },5000);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>


ES6模板字符串.html

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
let pros = [{id:4,name:'德芙巧克力',unit:'块',price:9.5},
{id:8,name:'辣条',unit:'包',price:3.5},
{id:11,name:'爆米花',unit:'盒',price:10.0}];
//ES5语法
// let html = '<tr><th>商品名称</th><th>单位</th><th>价格</th></tr>';
// for(let i = 0;i < pros.length;i ++) {
// let p = pros[i];
// html += '<tr><td><a href="javascript:show(' + p.id + ');">'
// + p.name + '</a></td><td>' + p.unit
// + '</td><td>' + p.price + '</td></tr>';
// }
//ES6语法:模板字符串不是使用单引号或者双引号引起来的,而是使用`
let html = `<tr><th>商品名称</th><th>单位</th><th>价格</th></tr>`;
for(let p of pros) {
html += `<tr>
<td>
<a href='javascript:show(${p.id});'>${p.name}</a>
</td>
<td>${p.unit}</td>
<td>${p.price}</td>
</tr>`;
}
document.getElementById('mytb').innerHTML = html;
}
function show(id){
alert('选择的商品id是:' + id);
}
let code = 'return `Hello,${name}`';
let fn = new Function('name',code);
// function fn(name){
// return `Hello,${name}`;
// }
console.log(fn('Ktty'));
let fun = n => `Hello,${n}`;
console.log(fun('张三'));
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table id="mytb" border="1">
</table>
</body>
</html>

ES6中的类.html

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<script>
//ES5语法定义类
// let Person = function(n,a){
// this.name = n;
// this.age = a;
// }
// //覆盖Person类的toString方法
// Person.prototype.toString = function(){
// console.log(123);
// }
// Person.prototype.study = function(){
// console.log('正在学习');
// }
// //定义静态的方法
// Person.test = function(){
// console.log('人类测试');
// }
//ES6语法定义类
class Person{
//定义构造函数
constructor(n,a){
this.name = n;
this.age = a;
}
toString(){
return '姓名是:' + this.name
+ ',年龄是:' + this.age;
}
study(){
console.log('正在学习');
}
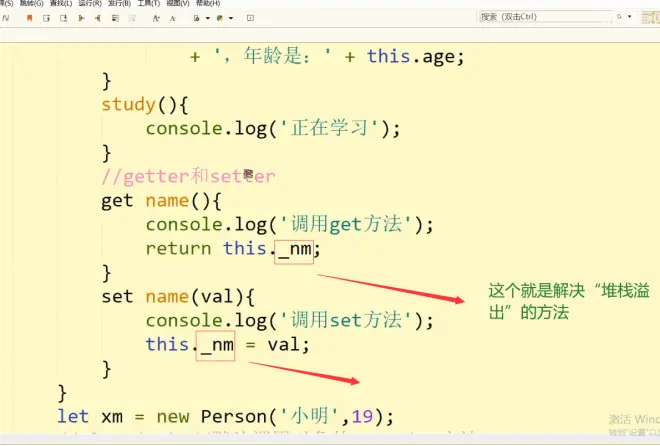
//getter和setter
get name(){//当获取对象的name属性时就会触发get name函数
console.log('调用get方法');
return this._nm;
}
set name(val){//当给对象的name属性赋值时会触发set name函数
console.log('调用set方法');
this._nm = val;
}
//定义静态的方法:只能通过类名点出来调用,不能通过对象点出来调用
static test(){
console.log('人类测试');
}
}
let xm = new Person('小明',19);
//alert(xm);//默认调用对象的toString方法
//xm.study();
//xm.name = 'Kite';
//console.log(xm.name);
//Person.test();
class Father{
constructor(money){
console.log('调用父类的构造方法');
this.account = money;
}
cost(){
console.log('父亲花钱了');
}
}
class Son extends Father{
constructor(m){
super(m);//调用父类中的构造方法
console.log('调用子类中的构造方法');
}
cost(){//覆盖了父类中的cost方法
console.log('儿子花钱了');
}
}
let s = new Son(200000);
console.log(s.account);
s.cost();
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>



