Unity_Addressable_Content update builds(更新内容构建)
The Addressables package includes tools that you can use to reduce the size of updates to the content you distribute remotely.
译:Addressables 包含了一些工具,可以帮助你减少远程分发的内容更新的大小,其中包括:
The content update tools include:
译:
Check for Content Update Restrictions tool: prepares your group organization for a content update build based on group settings译:Check for Content Update Restrictions 工具:根据组设置为内容更新构建准备组织
Update a Previous Build script: a build script that performs the content update build译:Update a Previous Build 脚本:执行内容更新构建的脚本
IMPORTANT
You must save the addressables_content_state.bin file produced by the Default Build Script for each build that you intend to update in the future. This file is updated every time you run the build script. Be sure to save the version produced for the content build that you publish. See Settings for relevant Addressable Settings that handle the use of the previous content state file.
译:对于您打算在未来进行更新的每个构建,都必须保存由默认构建脚本生成的 addressablescontentstate.bin 文件。每次运行构建脚本时,该文件都会更新。请确保保存您发布的内容构建所生成的版本。有关处理先前内容状态文件的相关 Addressable 设置,请参见设置。
For information on how to set up your Addressable groups for content updates, see Group settings.
译:有关如何为内容更新设置 Addressable 组的信息,请参见组设置。
For information on how to perform a content update build, see Building content updates.
译:有关如何执行内容更新构建的信息,请参见构建内容更新。
For general information about how content updates work, including examples, see Overview.
译:有关内容更新的概述信息,包括示例,请参见概述。
NOTE
On platforms that provide their own patching systems (such as Switch or Steam) or that do not support remote content distribution, do not use content update builds. Every build of your game should be a complete fresh content build. (In this case you can discard or ignore the addressables_content_state.bin file that is generated after each build for the platform.)
译:在提供自己的修补系统(例如 Switch 或 Steam)或不支持远程内容分发的平台上,请勿使用内容更新构建。您的游戏的每个构建都应该是一个完整的新内容构建。(在这种情况下,您可以丢弃或忽略为每个平台生成的 addressablescontentstate.bin 文件。)
Overview
When you distribute content remotely, you can make content changes without needing to rebuild and republish your entire application. When the Addressables system initializes at runtime, it checks for an updated content catalog. If one exists, the system downloads the new catalog and, when it loads assets, downloads the newer versions of all your AssetBundles.
译:当您远程分发内容时,您可以进行内容更改,而无需重新构建和重新发布整个应用程序。当 Addressables 系统在运行时初始化时,它会检查是否存在更新的内容目录。如果存在,则系统会下载新目录,并在加载资产时下载所有 AssetBundle 的新版本。
However, when you rebuild all of your content with a new content catalog, installed players must also redownload all of your remote AssetBundles, whether the assets in them have changed or not. If you have a large amount of content, redownloading everything can take a significant amount of time and may hurt player retention. To make this process more efficient, the Addressables package provides tools that you can run to identify changed assets and to produce a content update build.
译:但是,当您使用新的内容目录重新构建所有内容时,已安装的玩家必须重新下载所有远程 AssetBundle,无论其中的资产是否发生了变化。如果您有大量的内容,重新下载所有内容可能需要很长时间,并可能会影响玩家的留存率。为使此过程更加高效,Addressables 包提供了一些工具,可以运行这些工具来识别已更改的资产并生成内容更新构建。
The following diagram illustrates how you can use the Addressables tools to produce smaller content updates that only require your players to download new or changed content:
译:以下图表说明了您可以如何使用 Addressables 工具来生成更小的内容更新,从而只需要玩家下载新的或更改的内容:

The workflow for reducing the size of content updates
When you release your full application, you first build your Addressables content, as normal, and then make a player build. The player build contains your local AssetBundles and you upload your remote AssetBundles to your Content Delivery Network (CDN) or other hosting service.
译:发布完整应用程序时,您首先按照正常流程构建Addressables内容,然后制作玩家构建。玩家构建包含本地AssetBundles,您将远程AssetBundles上传到内容交付网络(CDN)或其他托管服务中。
The Default Build Script that produces your Addressables content build always creates the addressables_content_state.bin file, which is required to efficiently publish content-only updates. You must save this file for each published full application release (on every platform).
译:默认构建脚本始终会创建addressablescontentstate.bin文件,该文件需要用于高效地发布仅内容更新。您必须为每个发布的完整应用程序版本(在每个平台上)保存此文件。
Between full application releases, which require your users to download and install a new player build, you can make changes to your Addressable assets in the project. (Since AssetBundles do not include code, do not make code changes in the version of your project that you use to develop your asset changes.) You can change both local and remote assets.
译:在需要用户下载和安装新的玩家构建的完整应用程序版本之间,您可以在项目中更改Addressable资产。(由于AssetBundles不包含代码,请不要在用于开发资产更改的版本中进行代码更改。)您可以更改本地和远程资产。
When you are ready to publish a content update, we recommend running the Check Content Update Restrictions tool manually, or making sure the check is run as part of the update build process. See the section on Settings for more information. This check examines the addressables_content_state.bin file and moves changed assets to a new remote group, according to the settings of the group they are in.
译:当您准备发布内容更新时,我们建议手动运行Check Content Update Restrictions工具,或确保检查作为更新构建过程的一部分运行。有关更多信息,请参阅设置部分。此检查会检查addressablescontentstate.bin文件,并根据它们所在组的设置将更改的资产移动到新的远程组。
To build the updated AssetBundles, run the Update a Previous Build script. This tool also uses the addressables_content_state.bin file. It rebuilds all of your content, but produces a modified catalog that accesses unchanged content from their original AssetBundles and changed content from the new AssetBundles.
译:要构建更新的AssetBundles,请运行Update a Previous Build脚本。此工具也使用addressablescontentstate.bin文件。它会重新构建所有内容,但会生成一个修改后的目录,该目录从其原始AssetBundles访问未更改的内容和从新的AssetBundles访问更改的内容。
The final step is to upload the updated content to your CDN. (You can upload all the new AssetBundles produced or just those with changed names -- bundles that haven't changed use the same names as the originals and will overwrite them.)
译:最后一步是将更新后的内容上传到您的CDN。(您可以上传所有新产生的AssetBundles或仅上传具有更改名称的AssetBundles-未更改的bundle使用与原始名称相同的名称并将覆盖它们。)
You can make additional content updates following the same process. Always use the addressables_content_state.bin file from your original release.
译:您可以按照相同的流程进行其他内容更新。始终使用原始发布的addressablescontentstate.bin文件。
See Building content updates for step-by-step instructions.
译:有关详细说明,请参见构建内容更新的逐步说明。
When a full rebuild is required
Addressables can only distribute content, not code. As such, a code change generally requires a fresh player build, and usually a fresh build of content. Although a new player build can sometimes reuse old, existing content from a CDN, you must carefully analyze whether the type trees in the existing AssetBundles are compatible with your new code. This is advanced territory to explore carefully.
译:Addressables只能分发内容,而不能分发代码。因此,代码更改通常需要全新的玩家构建,通常还需要全新的内容构建。尽管新的玩家构建有时可以重用旧的现有内容,但必须仔细分析现有AssetBundles中的类型树是否与新代码兼容。这是需要仔细探索的高级领域。
Note that Addressables itself is code, so updating Addressables or Unity version likely requires that you create a new player build and fresh content builds.
译:请注意,Addressables本身是代码,因此更新Addressables或Unity版本可能需要创建新的玩家构建和全新的内容构建。
Settings
To publish content updates, your application must already use a remote catalog and host its remote content on an accessible server. See Enabling remote distribution for information about setting up content hosting and distribution.
译:要发布内容更新,您的应用程序必须已经使用远程目录,并将其远程内容托管在可访问的服务器上。有关设置内容托管和分发的信息,请参阅启用远程分发。
In addition to enabling remote content distribution, you should also consider how to set each group's Update Restriction settings. These settings determine how the Check for Content Update Restriction tool treats changed content in your groups. Choose appropriate settings to help minimize the download size of your content updates. See Group Update Restriction settings.
译:除了启用远程内容分发之外,您还应该考虑如何设置每个组的Update Restriction设置。这些设置确定Check for Content Update Restriction工具如何处理组中更改的内容。选择适当的设置,以帮助最小化内容更新的下载大小。请参阅Group Update Restriction设置。
The Addressable Asset Settings also contains a section for updating a previous build.
译:Addressable Asset设置还包含用于更新先前构建的部分。
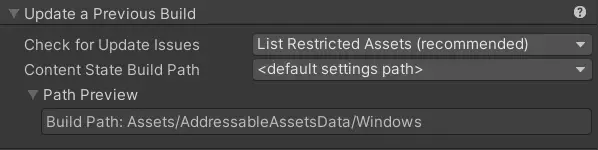
The two settings are Check For Update Issues which informs the system on if we should run the Check For Content Update Restrictions check automatically, and how to handle issues that are detected. The second is the Content State Build Path. This location serves two purposes:
译:这两个设置是Check For Update Issues,它通知系统是否应自动运行Check for Content Update Restrictions检查,以及如何处理检测到的问题。第二个是Content State Build Path。此位置具有两个目的:
It indicates where new Content Builds should put the previous state file译:它指示新的Content Builds应该将先前的状态文件放置在哪里
This is the location that Update a Previous Build attempts to pull the previous state file from automatically.译:这是Update a Previous Build尝试自动从中拉取先前状态文件的位置。
The Content State Build Path can be a remote location, should you want to have a shared previous state file on a server. The system handles remote locations for the previous state file a little differently.
译:Content State Build Path可以是远程位置,如果您希望在服务器上共享先前状态文件,则可以使用它。系统会稍微不同地处理以前的状态文件的远程位置。
New Content Builds place the previous state file to the
ContentUpdateScript.PreviousContentStateFileCachePath, which isLibrary/com.unity.addressables/AddressablesBinFileDownload/by default.译:新内容构建将先前的状态文件放置在ContentUpdateScript.PreviousContentStateFileCachePath中,它默认为Library/com.unity.addressables/AddressablesBinFileDownload/。Update a Previous Build downloads the remote previous state file to
ContentUpdateScript.PreviousContentStateFileCachePathand then reads the file like normal. If the file does not exist at the remote location, but one has already been placed in the cache path, the system loads the local file.译:Update a Previous Build将远程先前状态文件下载到ContentUpdateScript.PreviousContentStateFileCachePath,然后像正常文件一样读取文件。如果在远程位置不存在该文件,但已经在缓存路径中放置了一个文件,则系统会加载本地文件。
Another setting to consider if you want to update content on the fly (rather than at application startup), is the Unique Bundle IDs setting. Enabling this option can make it easier to load updated AssetBundles in the middle of an application session, but typically makes builds slower and updates larger. See Unique Bundle IDs setting.
译:如果您想要在应用程序会话的中间更新AssetBundles,则应考虑另一个设置:Unique Bundle IDs设置。启用此选项可以使更新的AssetBundles更容易加载,但通常会使构建速度变慢并使更新更大。请参见Unique Bundle IDs设置。
Group Update Restriction settings
For each group in your project, the Update Restriction schema determines how a Group, and its assets, are handled in a content update. The setting is:
译:对于项目中的每个组,Update Restriction架构确定如何处理内容更新中的组及其资产。设置是:
Prevent Updates: When toggled, the system treats assets in that group as static content that you expect to update infrequently, if at all. All local content should use this setting.译:阻止更新:切换后,系统将该组中的资产视为您希望不经常更新(如果有的话)的静态内容。所有本地内容都应使用此设置。
Choose the setting based on the type of content in a group and how frequently you expect to update that content (between full player builds of your application).
译:根据组中的内容类型以及您希望更新该内容的频率(在应用程序的完整播放器构建之间)选择设置
You can change content in a group no matter which setting you choose. The difference is how the Check for Content Update Restrictions and Update Previous Build tools treat the assets in the group and ultimately, how the installed applications access the updated content.
译:无论选择哪种设置,您都可以更改组中的内容。不同之处在于“检查内容更新限制”和“更新以前的构建”工具如何处理组中的资产,以及最终安装的应用程序如何访问更新的内容
IMPORTANT
Do NOT change the Update Restriction setting of a group unless you are performing a full build. If you change your group settings before a content update, Addressables cannot generate the correct changes needed for the update build.
译:除非您正在执行完整构建,否则不要更改组的更新限制设置。如果您在内容更新之前更改了组设置,Addressables 将无法生成更新构建所需的正确更改
Prevent Updates Enabled (static content)
When you enable Prevent Updates, the Check for Content Update Restrictions tool moves any changed assets to a new group, which is set to build and load from your remote paths. This is the same check that can be automatically integrated with Updating a Previous Build. Regardless of if you manually run the tool, or let Update a Previous Build handle the check automatically, the subsequent content update sets up the remote catalog so that the changed assets are accessed from the new bundles, but the unchanged assets are still accessed from the original bundles.
译:当您启用Prevent Updates时,Check for Content Update Restrictions工具会将任何更改的资产移动到一个新组,该组设置为从您的远程路径构建和加载。这是可以与更新以前的版本自动集成的相同检查。无论您是手动运行该工具,还是让Update a Previous Build自动处理检查,后续内容更新都会设置远程目录,以便从新包访问更改的资产,但仍从原始捆绑。
NOTE
Although the update build produces versions of the original bundles without the changed assets, installed applications do not download these bundles unless the locally cached version is deleted for some reason.
译:尽管更新构建生成原始包的版本而没有更改资产,但已安装的应用程序不会下载这些包,除非本地缓存的版本因某种原因被删除
Organize content that you don't expect to update frequently in groups set to groups with Prevent Updates. enabled. You can safely set up these groups to produce fewer, larger bundles since your users usually won't need to download these bundles more than once.
译:将您不希望经常更新的内容组织到设置为阻止更新的组中。启用。您可以安全地设置这些组以生成更少、更大的捆绑包,因为您的用户通常不需要多次下载这些捆绑包
Any groups that you intend to load from the local load path should always be set to Prevent Updates. Likewise, any groups that produce large, remote bundles should also be set to Prevent Updates so that your users only need to download the changed assets if you do end up changing assets in these groups.
译:您打算从本地加载路径加载的任何组都应始终设置为Prevent Updates。同样,任何产生大型远程包的组也应设置为防止更新,以便您的用户仅在您最终更改这些组中的资产时才需要下载更改的资产
Prevent Updates Disabled (dynamic content)
When a group does not have Prevent Updates, then a content update rebuilds the entire bundle if any assets inside the group have changed. The Update a Previous Build script sets the catalog up so that installed applications load all assets in the group from the new bundles.
译:当组没有Prevent Updates时,如果组内的任何资产发生更改,内容更新将重建整个包。Update a Previous Build脚本会设置目录,以便已安装的应用程序从新包中加载组中的所有资产。
Organize content you expect to change frequently into groups with Prevent Updates disabled. Since all the assets in these groups are republished when any single asset changes, you should typically set up these groups to produce smaller bundles containing fewer assets.
译:将您希望经常更改的内容组织到禁用防止更新的组中。由于这些组中的所有资产都会在任何单个资产更改时重新发布,因此您通常应该设置这些组以生成包含较少资产的较小包
Unique Bundle IDs setting
The Addressable Asset settings contain an option, Unique Bundle IDs, that affect content update builds. You can evaluate whether you need to enable this option if you run into AssetBundle ID conflicts when updating your application catalog at runtime.
译:Addressable Asset 设置包含一个选项Unique Bundle IDs,它会影响内容更新构建。如果在运行时更新应用程序目录时遇到 AssetBundle ID 冲突,您可以评估是否需要启用此选项
Enabling the Unique Bundle IDs option allows you to load a changed version of an AssetBundle while the original bundle is still in memory. Building your AssetBundles with unique internal IDs makes it easier to update content at runtime without running into AssetBundle ID conflicts.
译:启用Unique Bundle IDs选项允许您在原始包仍在内存中时加载 AssetBundle 的更改版本。使用唯一的内部 ID 构建 AssetBundle 可以更轻松地在运行时更新内容,而不会遇到 AssetBundle ID 冲突
The option is not without drawbacks, however. When enabled, any AssetBundles containing assets that reference a changed asset must also be rebuilt. More bundles must be updated for a content update and all builds are slower.
译:然而,该选项并非没有缺点。启用后,还必须重建任何包含引用已更改资产的资产的 AssetBundle。必须更新更多捆绑包才能进行内容更新,并且所有构建速度都较慢。
You typically only need to use unique bundle IDs when you update content catalogs after the Addressable system has already initialized and you have started loading assets.
译:在 Addressable 系统已经初始化并且您已经开始加载资产之后更新内容目录时,您通常只需要使用唯一的包 ID。
You can avoid AssetBundle loading conflicts and the need to enable unique IDs using one of the following methods:
译:您可以使用以下方法之一避免 AssetBundle 加载冲突和启用唯一 ID 的需要:
Update the content catalog as part of Addressables initialization. By default, Addressables checks for a new catalog at initialization (as long as you don't enable the Only update catalogs manually option in your Addressable Asset settings). Choosing this method does preclude updating your application content in mid-session.译:作为 Addressables 初始化的一部分更新内容目录。默认情况下,Addressables 在初始化时检查新目录(只要您未在 Addressable Asset 设置中启用Only update catalogs manually选项)。选择此方法确实会排除在会话中期更新您的应用程序内容
Unload all remote AssetBundles before updating the content catalog. Unloading all your remote bundles and assets also avoids bundle name conflicts, but could interrupt your user's session while they wait for the new content to load.译:在更新内容目录之前卸载所有远程 AssetBundle。卸载所有远程包和资产也可以避免包名称冲突,但可能会在用户等待新内容加载时打断他们的会话
Building content updates
To build a content update, run the Update a Previous Build script:
译:要构建内容更新,请运行Update a Previous Build脚本
We recommend running the Check for Content Update Restrictions tool if you don't want the Update a Previous Build to run the check automatically.译:如果您不希望更新以前的版本自动运行检查,我们建议运行检查内容更新限制工具
Open the Addressables Groups window in the Unity Editor (Window > Asset Management > Addressables > Groups).译:在 Unity Editor 中打开Addressables Groups窗口( Window > Asset Management > Addressables > Groups)
From the Build menu on the toolbar, run the Update a Previous Build script.译:从工具栏上的构建菜单,运行更新以前的构建脚本
The build generates a content catalog, a hash file, and AssetBundles.
译:该构建生成一个内容目录、一个哈希文件和 AssetBundle
The generated content catalog has the same name as the catalog in the original application build, overwriting the old catalog and hash file. The application loads the hash file at runtime to determine if a new catalog is available. The system loads unmodified assets from existing bundles that were shipped with the application or that the application has already downloaded.
译:生成的内容目录与原始应用程序构建中的目录同名,覆盖旧目录和哈希文件。应用程序在运行时加载哈希文件以确定是否有新目录可用。系统从应用程序随附的或应用程序已下载的现有捆绑包中加载未修改的资产
The system uses the content version string and location information from the addressables_content_state.bin file to create the AssetBundles. Asset bundles that do not contain updated content are written using the same file names as those in the build selected for the update. If an AssetBundle contains updated content, a new bundle is generated that contains the updated content, with a new file name so that it can coexist with the original on your content hosting service. Only AssetBundles with new file names must be copied to the location that hosts your content (though you can safely upload them all).
译:系统使用 addressables_content_state.bin 文件中的内容版本字符串和位置信息来创建 AssetBundle。不包含更新内容的资产包使用与为更新选择的构建中的文件名相同的文件名编写。如果 AssetBundle 包含更新的内容,则会生成一个包含更新内容的新包,并使用新文件名,以便它可以与内容托管服务上的原始内容共存。只有具有新文件名的 AssetBundle 必须复制到托管您的内容的位置(尽管您可以安全地上传它们)
The system also builds AssetBundles for content that cannot change, such as any local AssetBundles, but you do not need to upload them to the content hosting location, as no Addressables Asset entries reference them.
译:系统还为无法更改的内容构建 AssetBundle,例如任何本地 AssetBundle,但您不需要将它们上传到内容托管位置,因为没有可寻址资产条目引用它们
Note that you should not change the build scripts between building a new player and making content updates (e.g., player code, Addressables). This could cause unpredictable behavior in your application.
译:请注意,您不应在构建新播放器和进行内容更新(例如,播放器代码、Addressables)之间更改构建脚本。这可能会导致您的应用程序出现不可预知的行为
Additionally, if you delete the local content bundles created by your Addressables build from the Project Library folder, attempts to load Assets in those bundles fail when you run your game or application in the Editor and use the Use Existing Build (requires built groups) Play Mode script.
译:此外,如果您从项目库文件夹中删除由 Addressables 构建创建的本地内容包,则当您在编辑器中运行游戏或应用程序并使用使用现有构建(需要构建组)时,尝试加载这些包中的资产会失败模式脚本
Check for Content Update Restrictions tool
The Check for Content Update Restrictions tool prepares your group organization for a content update build. The tool examines the addressables_content_state.bin file and and group settings. If a group's Update Restrictions option was set to Prevent Updates in the previous build, the tool gives you the option to move any changed assets to a new remote group. We recommend applying the suggested changes, or reverting changes to these assets, unless you have a specific reason not to. When you create the update build, the new catalog maps the changed assets to their new, remote AssetBundles, while still mapping the unchanged assets to their original AssetBundles. Checking for content update restrictions does not check groups with Prevent Updates disabled.
译:Check for Content Update Restrictions工具可让您的小组组织为内容更新构建做好准备。该工具检查addressables_content_state.bin文件和组设置。如果组的更新限制选项在之前的版本中设置为防止更新,该工具会为您提供将任何更改的资产移动到新的远程组的选项。我们建议应用建议的更改,或恢复对这些资产的更改,除非您有特定的理由不这样做。当您创建更新构建时,新目录将更改的资产映射到它们新的远程 AssetBundle,同时仍将未更改的资产映射到它们的原始 AssetBundle。检查内容更新限制不会检查组防止更新已禁用
To run the tool:
译:要运行该工具
Open the Addressables Groups window in the Unity Editor (Window > Asset Management > Addressables > Groups).译:在 Unity Editor 中打开Addressables Groups窗口( Window > Asset Management > Addressables > Groups)
In the groups window, run the Check for Content Update Restrictions from the toolbar Tools menu.译:在组窗口中,从工具栏的“工具”菜单运行“检查内容更新限制”
Review the group changes made by the tool, if desired. You can change the names of any new remote groups the tool created, but moving assets to different groups can have unintended consequences.译:如果需要,查看工具所做的组更改。您可以更改该工具创建的任何新远程组的名称,但将资产移动到不同的组可能会产生意想不到的后果
Important: Before you run the Check for Content Update Restrictions tool, you should make a branch with your version control system. The tool rearranges your asset groups in a way suited for updating content. Branching ensures that next time you ship a full player build, you can return to your preferred content arrangement.
译:重要提示:在运行检查内容更新限制工具之前,您应该使用版本控制系统创建一个分支。该工具以适合更新内容的方式重新排列您的资产组。分支确保下次您发布完整的播放器构建时,您可以返回到您首选的内容安排
Checking for content updates at runtime
You can add a custom script to periodically check whether there are new Addressables content updates. Use the following function call to start the update:
译:您可以添加一个自定义脚本来定期检查是否有新的 Addressables 内容更新。使用以下函数调用开始更新:
where List<string> contains the list of modified locator IDs. You can filter this list to only update specific IDs, or pass it entirely into the UpdateCatalogs API.
译:其中 List<string> 包含修改后的定位器 ID 列表。您可以过滤此列表以仅更新特定 ID,或将其完全传递到 UpdateCatalogs API
If there is new content, you can either present the user with a button to perform the update, or do it automatically. Note that it is up to the developer to make sure that stale Assets are released.
译:如果有新内容,您可以向用户显示一个按钮来执行更新,或者自动执行更新。请注意,由开发人员确保释放过时的资产
The list of catalogs can be null and if so, the following script updates all catalogs that need an update:
译:目录列表可以为空,如果是这样,以下脚本会更新所有需要更新的目录
The return value is the list of updated locators.
译:返回值是更新定位器的列表。
You may also want to remove any bundle cache entries that are no longer referenced as a result of updating the catalogs. If so, use this version of the UpdateCatalogs API instead where you can enable the additional parameter autoCleanBundleCache to remove any unneeded cache data:
译:您可能还想删除任何因更新目录而不再引用的包缓存条目。如果是这样,请改用此版本的 UpdateCatalogs API,您可以在其中启用附加参数autoCleanBundleCache以删除任何不需要的缓存数据
See AssetBundle caching for additional information about the bundle cache.
译:有关包缓存的更多信息,请参阅AssetBundle 缓存。
See Unique Bundle IDs setting for additional information about updating content at runtime.
译:有关在运行时更新内容的更多信息,请参阅唯一包 ID 设置
Content update examples
The following discussion walks through a hypothetical example to illustrate how Addressable content is handled during a content update. In this example, consider a shipped application built with the following Addressables groups:
译:以下讨论通过一个假设示例来说明在内容更新期间如何处理可寻址内容。在此示例中,考虑使用以下 Addressables 组构建的已发布应用程序:
Local_Static Remote_Static Remote_NonStatic
AssetA AssetL AssetX
AssetB AssetM AssetY
AssetC AssetN AssetZ
Note that Local_Static and Remote_Static are part of the Cannot Change Post Release groups.
译:请注意,Local_Static 和 Remote_Static 是 Cannot Change Post Release 组的一部分。
Since this version is live, existing players have Local_Static on their devices, and potentially have either or both of the remote bundles cached locally.
译:由于此版本已上线,现有玩家的设备上都有 Local_Static,并且可能在本地缓存了一个或两个远程包。
If you modify one Asset from each group (AssetA, AssetL, and AssetX), then run Check for Content Update Restrictions, the results in your local Addressable settings are now:
译:如果您修改每个组(AssetA、AssetL 和 AssetX)中的一个资产,然后运行Check for Content Update Restrictions,您本地可寻址设置中的结果现在是
Local_Static Remote_Static Remote_NonStatic content_update_group (non-static)
AssetX AssetA
AssetB AssetM AssetY AssetL
AssetC AssetN AssetZ
Note that the prepare operation actually edits the Cannot Change Post Release groups, which may seem counterintuitive. The key, however, is that the system builds the above layout, but discards the build results for any such groups. As such, you end up with the following from a player's perspective:
译:请注意,准备操作实际上编辑了 Cannot Change Post Release 组,这似乎有悖常理。然而,关键是系统构建了上述布局,但丢弃了任何此类组的构建结果。因此,从玩家的角度来看,您最终会得到以下结果
Local_Static
AssetA
AssetB
AssetC
The Local_Static bundle is already on player devices, which you can't change. This old version of AssetA is no longer referenced. Instead, it is stuck on player devices as dead data.
译:Local_Static 包已经在播放器设备上,您无法更改。不再引用旧版本的 AssetA。相反,它作为死数据停留在播放器设备上
Remote_Static
AssetL
AssetM
AssetN
The Remote_Static bundle is unchanged. If it is not already cached on a player's device, it will download when AssetM or AssetN is requested. Like AssetA, this old version of AssetL is no longer referenced.
译:Remote_Static 包没有变化。如果它还没有缓存在玩家的设备上,它将在请求 AssetM 或 AssetN 时下载。与 AssetA 一样,不再引用旧版本的 AssetL
Remote_NonStatic (old)
AssetX
AssetY
AssetZ
The Remote_NonStatic bundle is now old. You can delete it from the server or leave it there; either way it will not be downloaded from this point forward. If cached, it remains on player devices indefinitely unless you remove it. See AssetBundle caching for more information. Like AssetA and AssetL, this old version of AssetX is no longer referenced.
译:Remote_NonStatic 包现在已经过时了。您可以将其从服务器中删除或保留在那里;无论哪种方式,它都不会从此时开始下载。如果缓存,它会无限期地保留在播放器设备上,除非您将其删除。有关详细信息,请参阅AssetBundle 缓存。与 AssetA 和 AssetL 一样,不再引用旧版本的 AssetX
Remote_NonStatic (new)
AssetX
AssetY
AssetZ
The old Remote_NonStatic bundle is replaced with a new version, distinguished by its hash file. The modified version of AssetX is updated with this new bundle.
译:旧的 Remote_NonStatic 包被替换为新版本,以其哈希文件区分。AssetX 的修改版本使用这个新包更新
content_update_group
AssetA
AssetL
The content_update_group bundle consists of the modified Assets that will be referenced moving forward.
译:content_update_group 包包含修改后的资产,这些资产将在以后被引用
Note that the example above has the following implications:
译:请注意,上面的示例具有以下含义
Any changed local Assets remain unused on the user's device forever.译:任何更改的本地资产将永远不会在用户的设备上使用
If the user already cached a non-static bundle, they will need to redownload the bundle, including the unchanged Assets (in this instance, for example, AssetY and AssetZ). Ideally, the user has not cached the bundle, in which case they simply need to download the new Remote_NonStatic bundle.译:如果用户已经缓存了一个非静态包,他们将需要重新下载包,包括未更改的资产(在本例中,例如,AssetY 和 AssetZ)。理想情况下,用户没有缓存包,在这种情况下,他们只需要下载新的 Remote_NonStatic 包
If the user has already cached the Static_Remote bundle, they only need to download the updated asset (in this instance, AssetL via content_update_group). This is ideal in this case. If the user has not cached the bundle, they must download both the new AssetL via content_update_group and the now-defunct AssetL via the untouched Remote_Static bundle. Regardless of the initial cache state, at some point the user will have the defunct AssetL on their device, cached indefinitely despite never being accessed.译:如果用户已经缓存了 Static_Remote 包,他们只需要下载更新的资产(在本例中,AssetL 通过 content_update_group)。在这种情况下这是理想的。如果用户没有缓存 bundle,他们必须通过 content_update_group 下载新的 AssetL,并通过未触及的 Remote_Static bundle 下载现已失效的 AssetL。无论初始缓存状态如何,在某些时候用户将在他们的设备上拥有已失效的 AssetL,尽管从未被访问过,但会无限期地缓存
The best setup for your remote content will depend on your specific use case.
译:远程内容的最佳设置将取决于您的具体用例
How Content Update Handles Dependencies
Directly changing an asset is not the only way to have it flagged as needing to be rebuilt as part of a content update. Changing an asset's dependencies is a less obvious factor that gets taken into account when building an update.
译:直接更改资产并不是将其标记为需要作为内容更新的一部分进行重建的唯一方法。更改资产的依赖项是构建更新时考虑的不太明显的因素
As an example, consider the Local_Static group from the example above:
译:例如,考虑上例中的 Local_Static 组
Local_Static
AssetA
AssetB
AssetC
but now suppose the assets in this group have a dependency chain that looks like this: AssetA depends on Dependency1, which depends on Dependency2, AssetB depends on Dependency2, and AssetC depends on Dependency3 and all three dependencies are a mix of Addressable and non-Addressable assets.
译:但现在假设该组中的资产具有如下所示的依赖链:AssetA 依赖于 Dependency1,而 Dependency1 依赖于 Dependency2,AssetB 依赖于 Dependency2,AssetC 依赖于 Dependency3,所有三个依赖都是可寻址和不可寻址的混合资产
Now, if only Dependency1 is changed and Check For Content Update Restriction is run, the resulting project structure looks like:
译:现在,如果仅更改 Dependency1 并运行 Check For Content Update Restriction,则生成的项目结构如下所示
Local_Static content_update_group
AssetA
AssetB
AssetC
If only Dependency2 is changed:
译:如果只更改 Dependency2
Local_Static content_update_group
AssetA
AssetB
AssetC
Finally, if only Dependency3 is changed:
译:最后,如果只更改 Dependency3
Local_Static content_update_group
AssetA
AssetB
AssetC
This is because when a dependency is changed the entire dependency tree needs to be rebuilt.
译:这是因为当一个依赖被改变时,整个依赖树需要被重建
Let's take a look at one more example with the following dependency tree. AssetA depends on AssetB, which depends on Dependency2, AssetB depends on Dependency2, and AssetC depends on Dependency3. Now, if Dependency2 is changed, the project structure looks like:
译:让我们再看一个具有以下依赖关系树的示例。AssetA依赖AssetB,AssetB依赖Dependency2,AssetB依赖Dependency2,AssetC依赖Dependency3。现在,如果更改 Dependency2,项目结构如下所示
Local_Static content_update_group
AssetA
AssetB
AssetC
because AssetA relies on AssetB and AssetB relies on Dependency2. Since the entire chain needs to be rebuilt both AssetA and AssetB will get put into the content_update_group.
译:因为 AssetA 依赖 AssetB 而 AssetB 依赖 Dependency2。由于需要重建整个链,因此 AssetA 和 AssetB 都将被放入 content_update_group中

