【官方双语/合集】线性代数的本质 - 系列合集

[来自2023.5.29:似乎看的人还挺多?距离笔者写这篇notes已经有小半年了,由于笔者是物理系的,目前正在学量子场论(qft),这里我稍微推荐基本比较能让读者建立线代思想的书籍,以及进一步的学习,当然,这是按照物理系安排的方法来的,我猜数学人估计不会点进来看笔记doge:第一个要声明的是,这篇note里并无除此视频以外的内容,只不过稍微对视频中的内容有所解释,没有更多的延拓与理解,因此我推荐一些书籍:pku的那本《简明高等代数》的风格和3b1b的风格还是挺像的(线代部分,当然要是想学完高等代数也并非不可),值得一看。还有一本鼎鼎大名的书《Linear algebra done right》中译本叫《线性代数应该这样学》的书,尽管书的作者说这是为第二次学线性代数的学生准备的,但我仍然认为这是一本讲线代的思想讲的极其清楚的书籍,并且后面有讲一些谱理论和一点算子的思想,3b1b的可视化将是你理解线性代数的利器,如果我以后给我的学生讲线代,我估计会让他们把这系列看完,然后我再给他们讲done right;第二个有趣的点在于,右手定则在更广义的拓展上来自于Grassmann algebra的反对称性(感兴趣的可以看梁昆淼的《微分几何和广义相对论》讲外积那一节,或者你可以在b站搜索“当时月影已不在”,加入我们的学习群(私信即可,记得标注自己的年级以及方向),有写的更棒的讲义,这本讲义的作者就是这位up主,代数专业的,你看了后就会明白他写的多么好了),大概先说这么多,要是后面有物理系的学生对进一步学习感兴趣的话我再稍微写写doge]
linear algebra(basis is the words we describe linear space):
1:linear combination:if you fix one of those scalars and let the other one change its value freely,the tip of the resulting vector draws a straight line.(an intuitive and funny explanation)

2.span: the set of all possible vectors that you can reach with a linear combination of a given vectors is called the "span" of those two vectors.
3.linear dependent:

linear independent:

I prefer this way(since it could show all the basis have the same weight):

([doge]):

4.linear transformation(input--->output "map"):
definition:T(a+b)=T(a)+T(b)
T(ca)=c T(a)
inference:
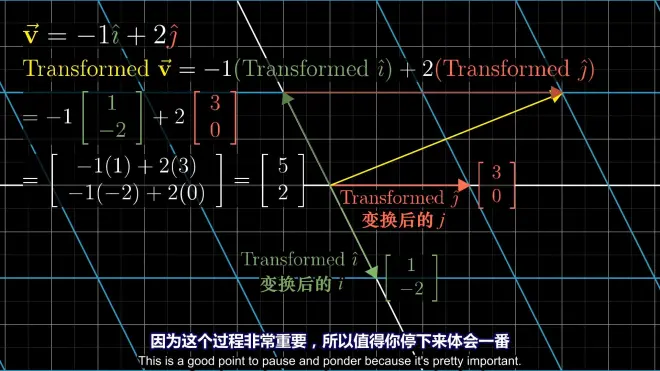
Matrix:[T(i) T(j)] (the langue we describe the linear transformation)
"shear"(“剪切”):

Matrix--vector multiplication:


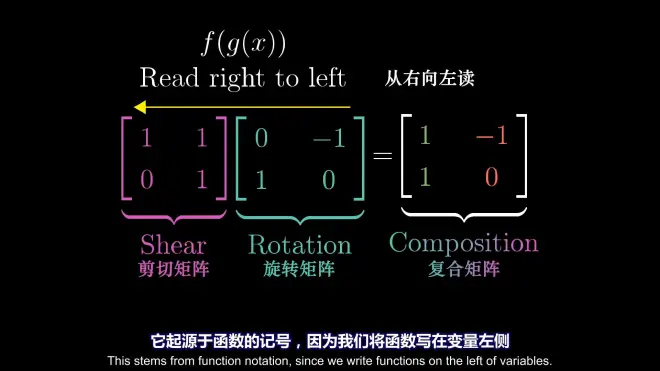
Satisfying associative law:
(M₁M₂)x=M₁(M₂x) (x是向量)
geometric way to explain it:
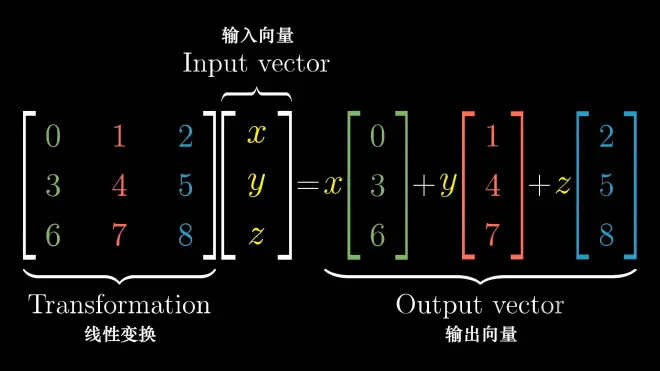
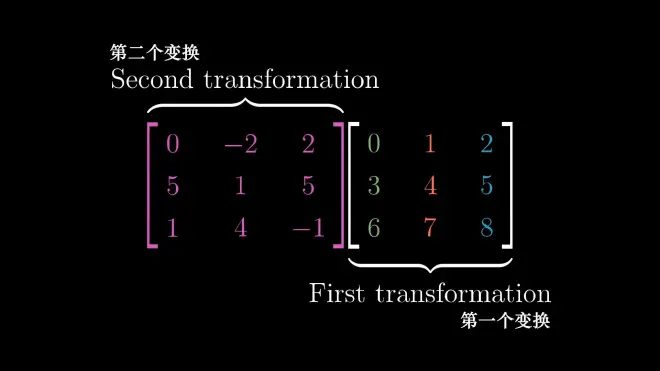
3-d space:

(值得一看的动漫)
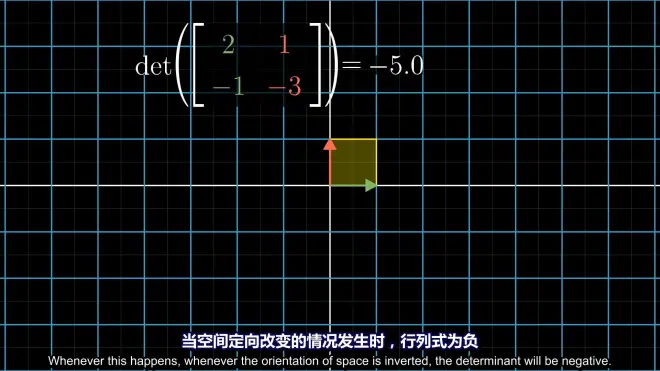
5.determinant:
definition(geometrically):

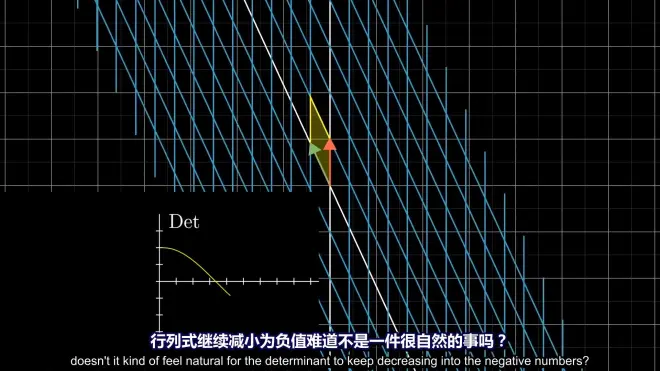
PS:行列式可为负:




3-d:

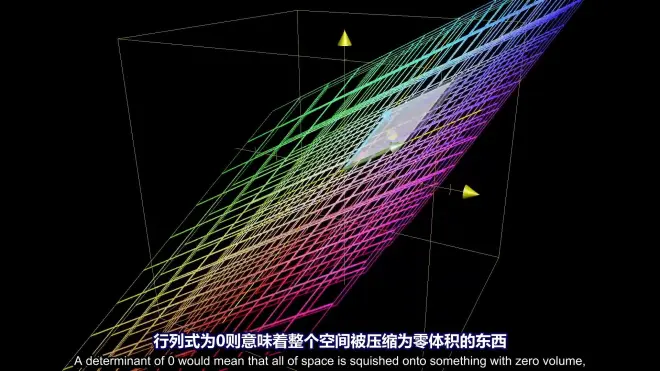
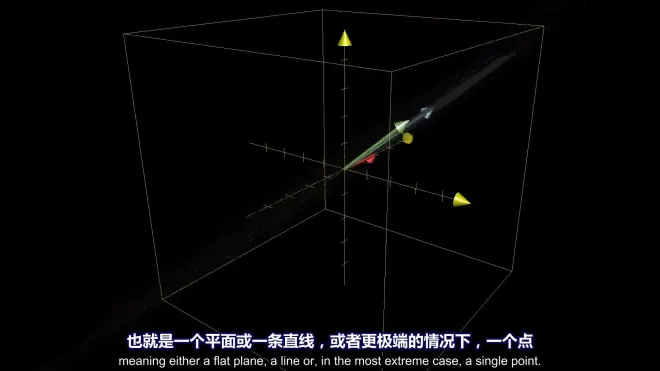
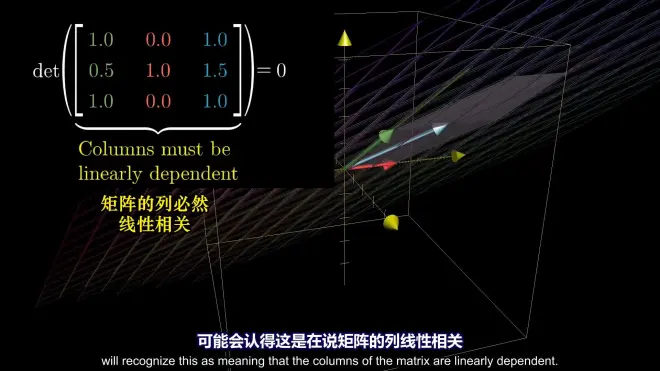
PS:变换矩阵的行列式为0时,它的Columns must be linearly dependent
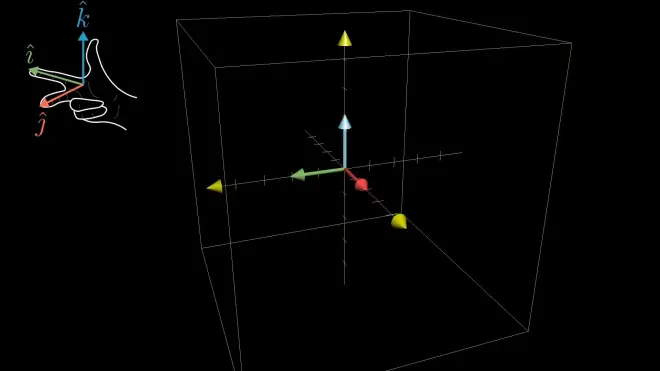
描述三维空间定向的方法(the famous"right hand rule"):


computing method(intuitive way):



algebraic operation(代数运算):
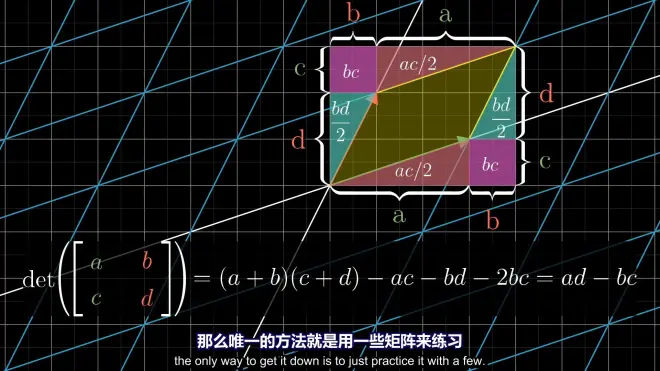
geometric way to explain it:
the stretching or compression of a linear space by two matrices is equivalent to the effect of the "sum matrix" on the linear space

6.solve linear system equations:
geometric interpretation:
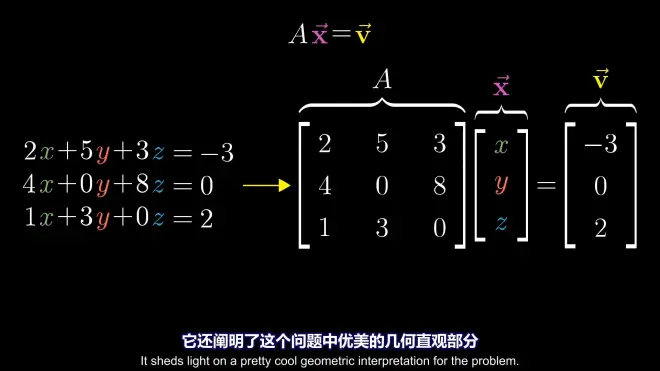
reason:
tip:column space--->row space(linear transformation)
det(M)≠o:
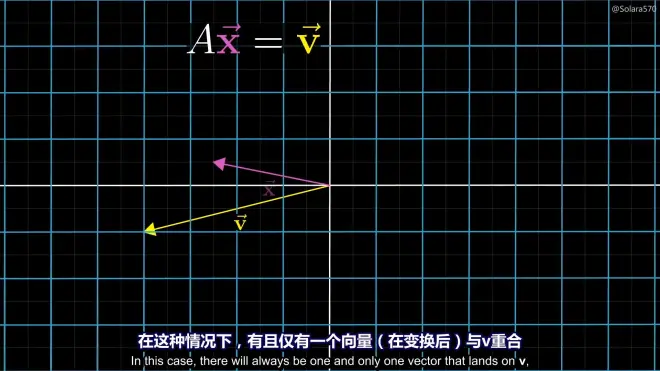
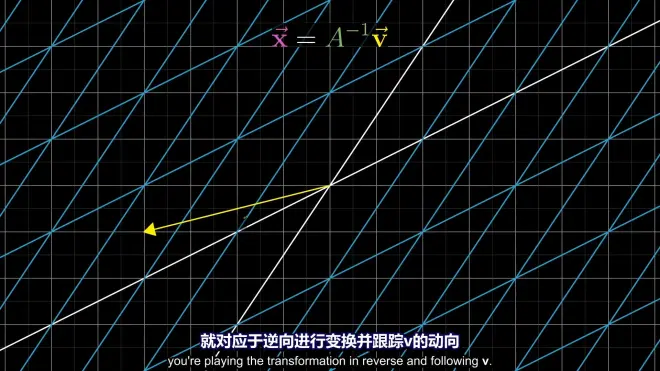
可通过逆向线性变换(逆矩阵)求解
notice:the reason is it's an injective map(单射)

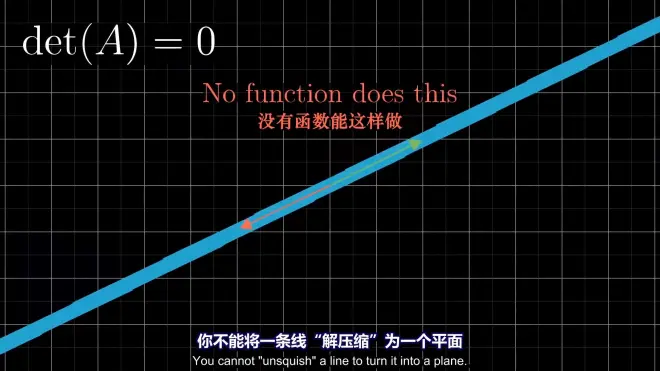
det(M)=0,no inverse
注:该线性变换的结果为向量,即该线性变换为“非单射”(非函数),任意升维线性变换("raised" rank)都是“非单射”形式的(这里把Matrix比作函数可能有些误导),如对一维向量使用“升维”线性变换将会得到一个平面

(需要在transformation后存在解, "eigenvector")


Rank("秩"的概念):

the dimension of the column space(
column space:the "span" of the linearly transformed vector)

null space("Kernel",核):the span of the vectors that becomes the zero vector after the linear transformation.
非方阵:
3 by 2:

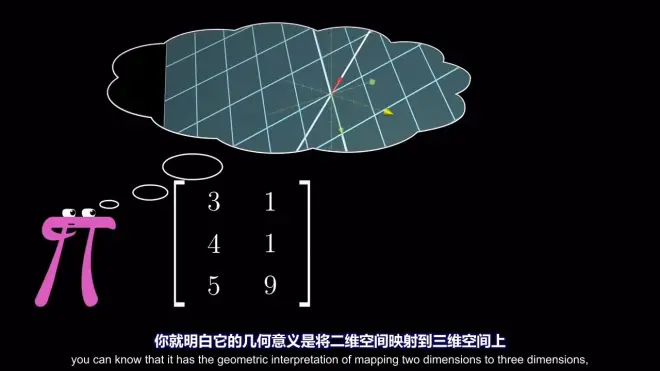
2 by 3:

7.duality property and dot product
非方阵与投影(这里以2 by 2 matrix举例)
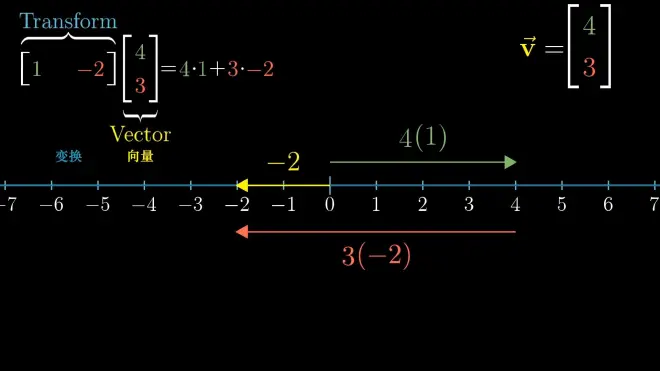

duality property:

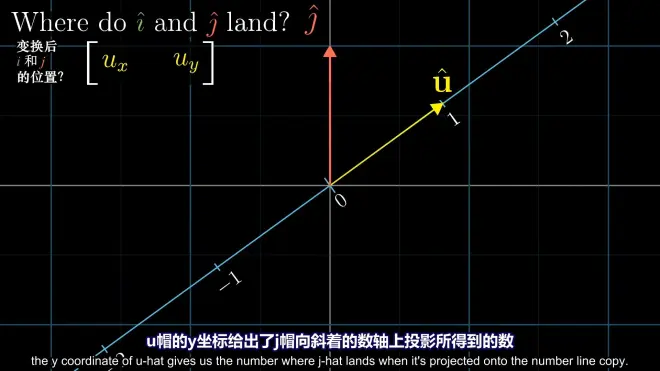
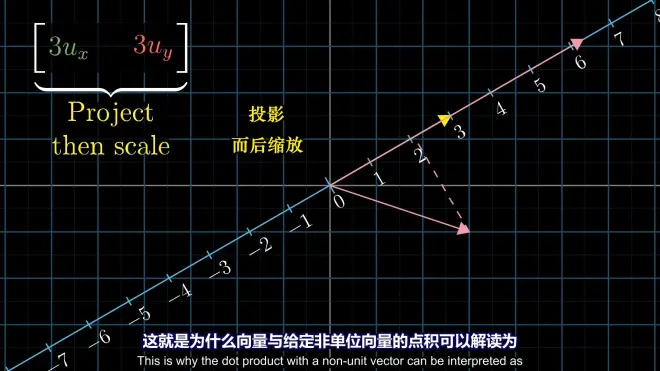
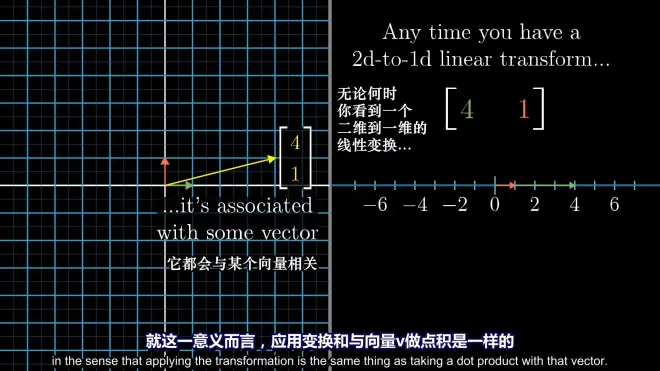
dot product is equivalent to the projection of the basis onto the dual vector (the geometric meaning of the dot product)
8.cross product(linear transformation and duality property) :
determinant的结果是一个number,因此它与一个三维到一维的线性变换有关(这里以三维到一维为例)
我们知道,三维到一维的线性变换可等价为“该向量”对dual vector的投影
同上,这个dual vector即为叉积的几何意义

定义linear transformation





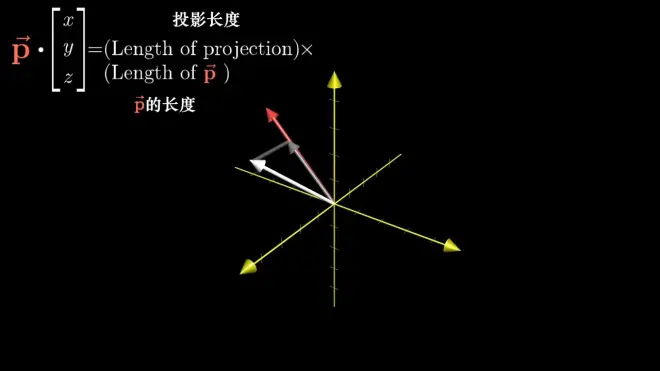
[若考虑输入任意 "x,y,z" 向量,该计算的几何意义为该平行六面体的体积,'x,y,z'向量对v,w平面上的投影与v,w平面面积的乘积,同样的,它与对偶向量(长度为v,w的平面面积值,不带有物理意义,行列式)和"x,y,z"向量的点积等价]

9.Transformation of basis
other's language(other basis)

(PS:2,1 and -1,1 are "our language"or"our vector space".)

make 2,1 -1,1 be basis(1,0 0,1)

